Antihypertensive effects of new dihydropyridine derivatives on phenylephrine-raised blood pressure in rats
- PMID: 28003844
- PMCID: PMC5168887
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.194897
Antihypertensive effects of new dihydropyridine derivatives on phenylephrine-raised blood pressure in rats
Abstract
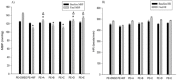
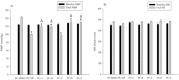
Changes in the substitutions at C-3 and C-5 positions of 4-(1-methyl-5-nitro-2-imidazolyl) dihydropyridine analogs of nifedipine have led to changes in potency of the compounds. The objective of the present study was to examine the hypotensive effects of 5 newly synthesized dihydropyridine derivatives of nifedipine in rats with phenylephrine-raised blood pressure. Anesthetized Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly assigned to 19 groups of 7 animals each. Control group received the vehicle dimethylsulfoxide (0.05 mL), 3 groups were given nifedipine at 100, 300, or 1000 μg/kg, and 5 other groups each composed of 3 subgroups administered one of the 5 new dihydropyridine compound at 100, 300, or 1000 μg/kg. All animals were initially infused with 20 µg/kg/min phenylephrine for 45 min, and were then given a bolus of either dimethylsulfoxide, nifedipine, or new dihydropyridine compounds 20 min after the commencement of phenylephrine infusion. Blood pressure and heart rate (HR) of the animals were measured before and at the end of phenylephrine infusion, or 25 min after injection of vehicle or compounds. Compared to dimethylsulfoxide, nifedipine, and new 1, 4-dihydropyridine derivatives caused significant reductions in MBP. Moreover, cyclohexyl propyl, phenyl butyl, and cyclohexyl methyl analogs of 1, 4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(1-methyl-5-nitro-2-imidazoyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylase at 100 μg/kg, phenyl butyl, and cyclohexyl methyl analogs at 300 μg/kg, and cyclohexyl methyl analogs at 1000 μg/kg reduced MBP similar to nifedipine. There was no significant difference between HR of all groups before and after administration of the compounds. The findings indicated that changes in substitution at C-3 and C-5 positions of 2-(1-methyl-5-nitro-2-imidazolyl) dihydropyridine analogs of nifedipine were associated with changes in hypotensive activity of the compounds.
Keywords: 1, 4-dihydropyridine; Arterial pressure; Nifedipine; Phenylephrine.
Figures

References
-
- Richard S. Vascular effects of calcium channel antagonists: new evidence. Drugs. 2005;65:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Haria M, Wagstaff AJ. Amlodipine. A reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in cardiovascular disease. Drugs. 1995;50(3):560–586. - PubMed
-
- Safak C, Simsek R. Fused 1,4-dihydropyridines as potential calcium modulatory compounds. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2006;6(7):747–755. - PubMed
-
- Triggle DJ. The 1,4-dihydropyridine nucleus: a pharmacophoric template part 1. Actions at ion channels. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003;3(3):215–223. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

