All-trans retinoic acid and genistein induce cell apoptosis in OVCAR-3 cells by increasing the P14 tumor suppressor gene
- PMID: 28003845
- PMCID: PMC5168888
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.194899
All-trans retinoic acid and genistein induce cell apoptosis in OVCAR-3 cells by increasing the P14 tumor suppressor gene
Abstract
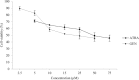
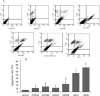
In this study, we evaluated the effects of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) alone or in combination with genistein (GEN) in p14 tumor suppressor gene and subsequent apoptosis of human ovarian carcinoma cells (OVCAR-3). The cells were treated with ATRA or GEN at concentrations of 50 and 25 μM respectively, either alone or in combination for 24 and 48 h. The cell viability was evaluated using 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazolyl-2)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The percentage of cell apoptosis was determined using flow cytometry and p14 gene expression was measured using real time PCR. The MTT results showed that in both ATRA and GEN treated groups, the cell viabilityviability in group treated for 48 h was significantly lower than group treated for 24 h. The flow cytometry results showed that the percentage of apoptotic cells in groups that treated with ATRA and GEN in combination for 24 h and 48 h was significantly more than all other tested groups. The real time results showed that the mRNA level of p14 in cells treated with both drugs for 48 h was significantly higher than all other groups. In conclusion, we confirm that GEN in combination with ATRA is an effective strategy to up regulate the p14 tumor suppressor gene and induce cell apoptosis in OVCAR-3 cell line.
Keywords: ATRA; Genistein; OVCAR-3; p14.
Figures


Similar articles
-
All-trans retinoic acid induces p53-depenent apoptosis in human hepatocytes by activating p14 expression via promoter hypomethylation.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jun 28;362(1):139-48. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.03.036. Epub 2015 Mar 27. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25827071
-
[Synergistic inhibitory effect of all-trans retinoic acid and 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 on growth of human hepatoma cell line HepG2].Ai Zheng. 2006 Dec;25(12):1470-6. Ai Zheng. 2006. PMID: 17166369 Chinese.
-
All trans retinoic acid modulates peripheral nerve fibroblasts viability and apoptosis.Tissue Cell. 2015 Feb;47(1):61-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2014.11.004. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Tissue Cell. 2015. PMID: 25532484
-
Combination treatment of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and γ-secretase inhibitor (DAPT) cause growth inhibition and apoptosis induction in the human gastric cancer cell line.Cytotechnology. 2018 Apr;70(2):865-877. doi: 10.1007/s10616-018-0199-3. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Cytotechnology. 2018. PMID: 29417442 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of all-trans retinoic acid-induced MiRNA expression in neoplastic cell lines: a systematic review.BMC Cancer. 2019 Aug 30;19(1):866. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6081-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31470825 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Combined dandelion extract and all-trans retinoic acid induces cytotoxicity in human breast cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 12;13(1):15074. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42177-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37700002 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic Acid Neutralizes the Effects of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1-Infected Cell Protein 0 (ICP0) in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells.Cureus. 2024 May 26;16(5):e61089. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61089. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38919217 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and in vitro characterization of retinoic acid-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone) micelles.Res Pharm Sci. 2017 Dec;12(6):465-478. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.217427. Res Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 29204175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Russo M, Russo GL, Daglia M, Kasi PD, Ravi S, Nabavi SF, et al. Understanding genistein in cancer: The “good” and the “bad” effects: A review. Food Chem. 2016;196:589–600. - PubMed
-
- Hashiguchi Y, Tsuda H, Yamamoto K, Inoue T, Ishiko O, Ogita S. Combined analysis of p53 and RB pathways in epithelial ovarian cancer. Hum pathol. 2001;32(9):988–996. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal A, Yang J, Murphy RF, Agrawal DK. Regulation of the p14ARF-Mdm2-p53 pathway: an overview in breast cancer. Exp Mol Pathol. 2006;81(2):115–122. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

