Laparoscopic posterior Colpotomy for a Cervico-vaginal Leiomyoma: hymen conservative technique
- PMID: 28003871
- PMCID: PMC5172573
Laparoscopic posterior Colpotomy for a Cervico-vaginal Leiomyoma: hymen conservative technique
Abstract
Background: Leiomyomas are the most common benign tumours of the uterus. The diagnosis, evaluation and treatment of prolapsed pedunculated submucous myoma may need vaginal access compromising sometimes the hymenal integrity. Laparoscopic management of a pedunculated submucous myoma in a Middle Eastern virgin patient is described as a safe alternative.
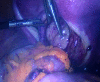
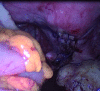
Case: A 20-year-old, nulliparous virgin woman presented to the outpatient clinic for irregular menstrual bleeding of 2 months duration. Imaging revealed a 5×5 cm solid mass in the cervico-vaginal location filling the vagina suggestive of a prolapsed pedunculated submucous leiomyoma. Due to the patient's desire of preserving her intact hymen, a laparoscopic posterior colpotomy was performed and the mass was removed successfully.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic posterior colpotomy, preserving the hymenal integrity in a virgin patient, provides excellent access and visualization and it is a safe tool for the management of a cervico-vaginal pedunculated submucous myoma by a skilled laparoscopic gynaecologic surgeon.
Keywords: Laparoscopy; colpotomy; hymen; hymenal integrity; leiomyoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mini-laparotomic Colpotomy for a Cervicovaginal Leiomyoma: Preservation of hymenal integrity.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2016 Mar;14(3):217-20. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2016. PMID: 27294222 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic Management of Huge Myoma Nascendi.J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017 Mar-Apr;24(3):347-348. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2016.09.003. Epub 2016 Sep 12. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017. PMID: 27632930
-
Massive prolapsed submucous fibroid treated with laparoscopic surgery: A case report.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019 Apr;45(4):942-946. doi: 10.1111/jog.13901. Epub 2019 Jan 25. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019. PMID: 30681230
-
Vaginal extraction of pelvic masses following operative laparoscopy.Surg Endosc. 2002 Dec;16(12):1691-6. doi: 10.1007/s00464-002-9043-z. Epub 2002 Jul 29. Surg Endosc. 2002. PMID: 12140631 Review.
-
Uncertainties about laparoscopic myomectomy during pregnancy: A lack of evidence or an inherited misconception? A critical literature review starting from a peculiar case.Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2015;24(4):189-94. doi: 10.3109/13645706.2014.987678. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2015. PMID: 25496138 Review.
Cited by
-
Hymen conservative techniques for vaginal surgery - a practical approach.Prz Menopauzalny. 2022 Mar;21(1):64-68. doi: 10.5114/pm.2022.113556. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Prz Menopauzalny. 2022. PMID: 35388280 Free PMC article.
-
Vaginal leiomyoma: medical imaging and diagnosis in a resource low tertiary hospital: case report.BMC Womens Health. 2020 Jan 21;20(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12905-020-0883-2. BMC Womens Health. 2020. PMID: 31964370 Free PMC article.
-
Hymen-Sparing Myomectomy: Innovative Laparoscopic Approach for Prolapsed Pedunculated Cervicovaginal Leiomyoma in a Virgin Case.Int J Womens Health. 2025 Jul 25;17:2313-2323. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S528452. eCollection 2025. Int J Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40735534 Free PMC article.
-
Cervical fibroids: the vaginal intracapsular myomectomy with classification by the fibroids' origin, growth directions, and localizations.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 May 9;12:1564667. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1564667. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40417667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists (AAGL): Advancing Minimally Invasive Gynecology Worldwide. AAGL practice report: practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of submucousleiomyomas. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:152–171. - PubMed
-
- Coventry DM. Anaesthesia for laparoscopic surgery. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1995;40:151–160. - PubMed
-
- Di Spiezio Sardo A, Zizolfi B, Calagna G, et al. Vaginohysteroscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of vaginal lesions. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2016;133:146–151. - PubMed
-
- Golan A, Zachalka N, Lurie S, et al. Vaginal removal of prolapsed pedunculated submucous myoma: a short, simple, and definitive procedure with minimal morbidity. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2005;271:11–13. - PubMed
-
- Kaivanara M. Virginity dilemma: Re-creating virginity through hymenoplasty in Iran. Cult Health Sex. 2016;18:71–83. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources