Development of a multiplex RT-PCR for simultaneous diagnosis of human metapneumovirus (HMPV) and human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) from clinical specimens
- PMID: 28004017
- PMCID: PMC5142592
- DOI: 10.1007/s13337-016-0348-2
Development of a multiplex RT-PCR for simultaneous diagnosis of human metapneumovirus (HMPV) and human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) from clinical specimens
Abstract
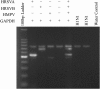
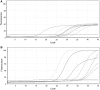
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) and human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) are ubiquitous respiratory viral pathogens. They belong to the family Paramyxoviridae (subfamily Pneumovirinae) and is responsible for acute respiratory tract infections in children, elderly and immunocompromised patients. We designed and tested a multiplex reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (mRT-PCR) as a cost-effective alternative to real-time PCR and cell culture based detection for HMPV and HRSV. The newly developed PCR was used to screen nasal/throat swab samples from 356 patients with suspected acute respiratory infection attending the Government Medical College, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India. The method was compared with a commercially available kit employing real time PCR, for its sensitivity and specificity. 53 (14.9 %) samples were positive for at least one tested pathogen by mRT-PCR. All except one among the positive samples showed similar pathogen profile when tested using real time PCR. 8 (15.1 %) among these 53 were positive for HRSVA, 33 (62.3 %) positive for HRSVB and 12 (22.6 %) were positive for HMPV. 17 (32.7 %) samples showed co-infections in them. Sensitivity and specificity of the mRT-PCR was comparable to that of the commercial kit. Our findings indicate that this newly developed mRT-PCR can be used as a cost-effective alternative for laboratory diagnosis of HMPV/HRSV infection and will significantly reduce diagnostic costs for these viruses in clinical settings.
Keywords: Acute respiratory infection; Human metapneumovirus; Human respiratory syncytial virus; Multiplex reverse transcriptase PCR; Real-time reverse transcriptase PCR.
Figures

References
-
- Bellau-Pujol S, Vabret A, Legrand L, Dina J, Gouarin S, Petitjean-Lecherbonnier J, Pozzetto B, Ginevra C, Freymuth F. Development of three multiplex RT PCR assays for the detection of 12 respiratory RNA viruses. J Virol Methods. 2005;12:53–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2005.01.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boivin G, Abed Y, Pelletier G, Ruel L, Moisan D, Cote S. Virological features and clinical manifestations associated with human metapneumovirus: a new paramyxovirus responsible for acute respiratory-tract infections in all age groups. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:1330–1334. doi: 10.1086/344319. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

