The citrus flavonoid naringenin confers protection in a murine endotoxaemia model through AMPK-ATF3-dependent negative regulation of the TLR4 signalling pathway
- PMID: 28004841
- PMCID: PMC5177915
- DOI: 10.1038/srep39735
The citrus flavonoid naringenin confers protection in a murine endotoxaemia model through AMPK-ATF3-dependent negative regulation of the TLR4 signalling pathway
Abstract
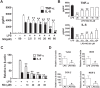
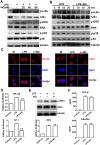
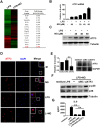
Excessive activation of the TLR4 signalling pathway is critical for inflammation-associated disorders, while negative regulators play key roles in restraining TLR4 from over-activation. Naringenin is a citrus flavonoid with remarkable anti-inflammatory activity, but the mechanisms underlying its inhibition of LPS/TLR4 signalling are less clear. This study investigated the molecular targets and therapeutic effects of naringenin in vitro and in vivo. In LPS-stimulated murine macrophages, naringenin suppressed the expression of TNF-α, IL-6, TLR4, inducible NO synthase (iNOS), cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX2) and NADPH oxidase-2 (NOX2). Naringenin also inhibited NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation. However, it did not affect the IRF3 signalling pathway or interferon production, which upregulate activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3), an inducible negative regulator of TLR4 signalling. Naringenin was demonstrated to directly increase ATF3 expression. Inhibition of AMPK and its upstream calcium-dependent signalling reduced ATF3 expression and dampened the anti-inflammatory activity of naringenin. In murine endotoxaemia models, naringenin ameliorated pro-inflammatory reactions and improved survival. Furthermore, it induced AMPK activation in lung tissues, which was required for ATF3 upregulation and the enhanced anti-inflammatory activity. Overall, this study reveals a novel mechanism of naringenin through AMPK-ATF3-dependent negative regulation of the LPS/TLR4 signalling pathway, which thereby confers protection against murine endotoxaemia.
Figures
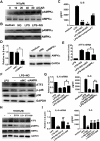



References
-
- Akira S. & Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4, 499–511 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Broz P. & Monack D. M. Newly described pattern recognition receptors team up against intracellular pathogens. Nat Rev Immunol 13, 551–565 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Mills K. H. TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol 11, 807–822 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Gay N. J., Symmons M. F., Gangloff M. & Bryant C. E. Assembly and localization of Toll-like receptor signalling complexes. Nat Rev Immunol 14, 546–558 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

