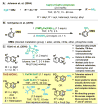
Non-Deprotonative Primary and Secondary Amination of (Hetero)Arylmetals
- PMID: 28004917
- PMCID: PMC5348115
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b12712
Non-Deprotonative Primary and Secondary Amination of (Hetero)Arylmetals
Abstract
Herein we disclose a novel method for the facile transfer of primary (-NH2) and secondary amino groups (-NHR) to heteroaryl- as well as arylcuprates at low temperature without the need for precious metal catalysts, ligands, excess reagents, protecting and/or directing groups. This one-pot transformation allows unprecedented functional group tolerance and it is well-suited for the amination of electron-rich, electron-deficient as well as structurally complex (hetero)arylmetals. In some of the cases, only catalytic amounts of a copper(I) salt is required.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rappoport Z, editor. The Chemistry of Anilines, Parts 1–2. John Wiley & Sons; Chichester: 2007.
-
- Scholz U, Schlummer B. Sci Synth. 2007;31b:1565.
-
-
For reviews on the Buchwald-Hartwig amination, see: Hartwig JF. Synlett. 1997;1997:329.Hartwig JF. Acc Chem Res. 1998;31:852.Hartwig JF. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 1998;37:2046.Wolfe JP, Wagaw S, Marcoux JF, Buchwald SL. Acc Chem Res. 1998;31:805.Surry DS, Buchwald SL. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2008;47:6338.Surry DS, Buchwald SL. Chem Sci. 2011;2:27.
-
-
-
For reviews on electrophilic amination, see: Daskapan T. ARKIVOC. 2011:230.Jarvo E, Barker T. Synthesis. 2011;2011:3954.Starkov P, Jamison TF, Marek I. Chem - Eur J. 2015;21:5278.Dong X, Liu Q, Dong Y, Liu H. Chem Eur J. 2016:22. doi: 10.1002/chem.201601607.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources