GRIL-seq provides a method for identifying direct targets of bacterial small regulatory RNA by in vivo proximity ligation
- PMID: 28005055
- PMCID: PMC5567838
- DOI: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.239
GRIL-seq provides a method for identifying direct targets of bacterial small regulatory RNA by in vivo proximity ligation
Abstract
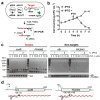
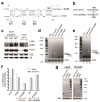
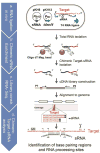
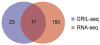
The first step in the post-transcriptional regulatory function of most bacterial small non-coding RNAs (sRNAs) is base pairing with partially complementary sequences of targeted transcripts. We present a simple method for identifying sRNA targets in vivo and defining processing sites of the regulated transcripts. The technique, referred to as global small non-coding RNA target identification by ligation and sequencing (GRIL-seq), is based on preferential ligation of sRNAs to the ends of base-paired targets in bacteria co-expressing T4 RNA ligase, followed by sequencing to identify the chimaeras. In addition to the RNA chaperone Hfq, the GRIL-seq method depends on the activity of the pyrophosphorylase RppH. Using PrrF1, an iron-regulated sRNA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, we demonstrated that direct regulatory targets of this sRNA can readily be identified. Therefore, GRIL-seq represents a powerful tool not only for identifying direct targets of sRNAs in a variety of environments, but also for uncovering novel roles for sRNAs and their targets in complex regulatory networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

