Mucin 4 and matrix metalloproteinase 7 as novel salivary biomarkers for periodontitis
- PMID: 28005264
- PMCID: PMC5347886
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.12670
Mucin 4 and matrix metalloproteinase 7 as novel salivary biomarkers for periodontitis
Abstract
Aim: Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease, characterized by irreversible destruction of tooth-supporting tissue including alveolar bone. We recently reported mucin 4 (MUC4) and matrix metalloproteinase 7 (MMP7) as highly associated with periodontitis in gingival tissue biopsies. The aim of this study was to further investigate the levels of MUC4 and MMP7 in saliva and gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) samples of patients with periodontitis.
Materials and methods: Saliva and GCF samples were collected from periodontitis patients and healthy controls. The levels of MUC4, MMP7, and total protein concentrations were analysed using ELISA or Bradford assay.
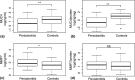
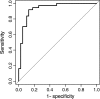
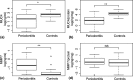
Results: MUC4 levels were significantly lower in saliva and GCF from periodontitis patients relative to healthy controls. MMP7 levels were significantly higher in saliva and GCF from periodontitis patients. Multivariate analysis revealed that MUC4 was significantly associated with periodontitis after adjusting for age and smoking habits and, moreover, that the combination of MUC4 and MMP7 accurately discriminated periodontitis from healthy controls.
Conclusions: MUC4 and MMP7 may be utilized as possible novel biomarkers for periodontitis.
Keywords: gingival crevicular fluid; matrix metalloproteinase 7; mucin 4; periodontitis; saliva.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Periodontology Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MUC4 and MMP7 in saliva and gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) in adolescents at West Bengal, India.Bioinformation. 2022 Mar 31;18(3):165-169. doi: 10.6026/97320630018165. eCollection 2022. Bioinformation. 2022. PMID: 36518149 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing periodontitis biomarkers in saliva, oral rinse and gingival crevicular fluid: A pilot study.J Clin Periodontol. 2021 Sep;48(9):1250-1259. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13479. Epub 2021 Jun 20. J Clin Periodontol. 2021. PMID: 33998029 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in gingival crevicular fluid and saliva of periodontitis patients.J Clin Periodontol. 1996 Dec;23(12):1127-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1996.tb01814.x. J Clin Periodontol. 1996. PMID: 8997658
-
The emerging role of small extracellular vesicles in saliva and gingival crevicular fluid as diagnostics for periodontitis.J Periodontal Res. 2022 Jan;57(1):219-231. doi: 10.1111/jre.12950. Epub 2021 Nov 13. J Periodontal Res. 2022. PMID: 34773636 Review.
-
Biomarkers of alveolar bone resorption in gingival crevicular fluid: A systematic review.Arch Oral Biol. 2018 Sep;93:12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.05.004. Epub 2018 May 22. Arch Oral Biol. 2018. PMID: 29800801
Cited by
-
Interfacial interactions of SERS-active noble metal nanostructures with functional ligands for diagnostic analysis of protein cancer markers.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 Apr 12;188(5):164. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04807-z. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 33844071 Review.
-
Impact of increased Porphyromonas gingivalis peptidylarginine deiminase (PPAD) T2 variant allele on oral microbiota composition and severity of chronic periodontitis.J Oral Microbiol. 2025 Mar 20;17(1):2479903. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2025.2479903. eCollection 2025. J Oral Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40123596 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of salivary alpha amylase and mucin-4 before and after non-surgical treatment of peri-implant mucositis.Int J Implant Dent. 2022 Jul 14;8(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40729-022-00429-z. Int J Implant Dent. 2022. PMID: 35834021 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary Redox Biomarkers in Selected Neurodegenerative Diseases.J Clin Med. 2020 Feb 12;9(2):497. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020497. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32059422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of (3S)-Vestitol on Peritoneal Macrophages.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Apr 29;15(5):553. doi: 10.3390/ph15050553. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al‐Azri, A. R. , Gibson, R. J. , Keefe, D. M. & Logan, R. M. (2013) Matrix metalloproteinases: do they play a role in mucosal pathology of the oral cavity? Oral Diseases 19, 347–359. - PubMed
-
- Andrianifahanana, M. , Agrawal, A. , Singh, A. P. , Moniaux, N. , van Seuningen, I. , Aubert, J. P. , Meza, J. & Batra, S. K. (2005) Synergistic induction of the MUC4 mucin gene by interferon‐gamma and retinoic acid in human pancreatic tumour cells involves a reprogramming of signalling pathways. Oncogene 24, 6143–6154. - PubMed
-
- Arpino, V. , Brock, M. & Gill, S. E. (2015) The role of TIMPs in regulation of extracellular matrix proteolysis. Matrix Biology 44–46, 247–254. - PubMed
-
- Balbin, M. , Fueyo, A. , Knauper, V. , Pendas, A. M. , Lopez, J. M. , Jimenez, M. G. , Murphy, G. & Lopez‐Otin, C. (1998) Collagenase 2 (MMP‐8) expression in murine tissue‐remodeling processes. Analysis of its potential role in postpartum involution of the uterus. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, 23959–23968. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

