Ectopic Adipose Tissue Storage in the Left and the Right Renal Sinus is Asymmetric and Associated With Serum Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Levels Increase
- PMID: 28005535
- PMCID: PMC5264268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.10.020
Ectopic Adipose Tissue Storage in the Left and the Right Renal Sinus is Asymmetric and Associated With Serum Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Levels Increase
Abstract
Objective: A potential mechanism by which obesity could promote hypertension and kidney diseases is through accumulation of adipose tissue in the renal sinus (RS). The aim of the study was to quantify RS and abdominal adipose tissue volumes and to evaluate serum kidney injury molecule (sKIM)-1 and fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-21 association with different adipose tissue compartments.
Methods: The cross-sectional study included 280 and follow-up study-40 asymptomatic participants; aged 38.30±4.10. For all study participants computed tomography examination was performed, sKIM-1 and FGF-21 levels were measured.
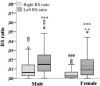
Results: The results indicated asymmetrical deposition of adipose tissue into the RS even after corresponding kidney volume adjustment. The cross-sectional and the follow-up studies showed that sKIM-1 level was positively associated with RS adipose tissue volume increase for both genders. FGF-21 was positively associated with RS and retroperitoneal adipose tissue amount.
Conclusions: Regardless of gender adipose tissue in RS accumulates asymmetrically-the left RS accumulates a significantly higher amount of adipose tissue. Thus, primarily RS adipose tissue effects should be assessed on the left kidney. Accumulation of adipose tissue in the RS is related with the visceral adipose amount, KIM-1 and FGF-21 concentration increase in the blood serum.
Keywords: Asymmetry; FGF-21; KIM-1; Obesity; Renal sinus; Visceral adipose tissue.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Bonventre J.V. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1): a urinary biomarker and much more. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009;24:3265–3268. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

