Cloning and Functional Analysis of Pax6 from the Hydrothermal Vent Tubeworm Ridgeia piscesae
- PMID: 28005979
- PMCID: PMC5179022
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168579
Cloning and Functional Analysis of Pax6 from the Hydrothermal Vent Tubeworm Ridgeia piscesae
Abstract
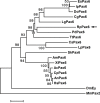
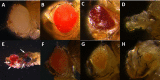
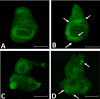
The paired box 6 (Pax6) gene encodes a transcription factor essential for eye development in a wide range of animal lineages. Here we describe the cloning and characterization of Pax6 gene from the blind hydrothermal vent tubeworm Ridgeia piscesae (RpPax6). The deduced RpPax6 protein shares extensive sequence identity with Pax6 proteins from other species and contains both the paired domain and a complete homeodomain. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that it clusters with the corresponding sequence from the closely related species Platynereis dumerilii (P. dumerilii) of Annelida. Luciferase reporter assay indicate that RpPax6 protein suppresses the transcription of sine oculis (so) in D. melanogaster, interfering with the C-terminal of RpPax6. Taking advantage of Drosophila model, we show that RpPax6 expression is not able to rescue small eye phenotype of ey2 mutant, only to cause a more severe headless phenotype. In addition, RpPax6 expression induced apoptosis and inhibition of apoptosis can partially rescue RpPax6-induced headless phenotype. We provide evidence RpPax6 plays at least two roles: it blocks the expression of later-acting transcription factors in the eye development cascade, and it promotes cell apoptosis. Our results indicate alternation of the Pax6 function may be one of the possible causes that lead the eye absence in vestimentiferan tubeworms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Relaix F. Pax genes: Master regulators of development and tissue homeostasis. Semin Cell DevBiolI. 2015; 44:62–63. - PubMed
-
- Gehring WJ, Ikeo K. Pax 6: mastering eye morphogenesis and eye evolution. Trends Genet. 1999; 15(9):371–377. - PubMed
-
- Callaerts P, Halder G, Gehring WJ. PAX-6 in development and evolution. Annu Rev Neuro Sci. 1997; 20(1):483–532. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

