A Network of Chromatin Factors Is Regulating the Transition to Postembryonic Development in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 28007841
- PMCID: PMC5295584
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.116.037747
A Network of Chromatin Factors Is Regulating the Transition to Postembryonic Development in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
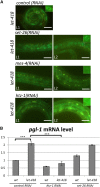
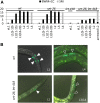
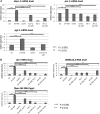
Mi2 proteins are evolutionarily conserved, ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers of the CHD family that play key roles in stem cell differentiation and reprogramming. In Caenorhabditis elegans, the let-418 gene encodes one of the two Mi2 homologs, which is part of at least two chromatin complexes, namely the Nucleosome Remodeling and histone Deacetylase (NuRD) complex and the MEC complex, and functions in larval development, vulval morphogenesis, lifespan regulation, and cell fate determination. To explore the mechanisms involved in the action of LET-418/Mi2, we performed a genome-wide RNA interference (RNAi) screen for suppressors of early larval arrest associated with let-418 mutations. We identified 29 suppressor genes, of which 24 encode chromatin regulators, mostly orthologs of proteins present in transcriptional activator complexes. The remaining five genes vary broadly in their predicted functions. All suppressor genes could suppress multiple aspects of the let-418 phenotype, including developmental arrest and ectopic expression of germline genes in the soma. Analysis of available transcriptomic data and quantitative PCR revealed that LET-418 and the suppressors of early larval arrest are regulating common target genes. These suppressors might represent direct competitors of LET-418 complexes for chromatin regulation of crucial genes involved in the transition to postembryonic development.
Keywords: P granules; chromatin; development; genome-wide RNAi screen; germline.
Copyright © 2017 Erdelyi et al.
Figures



References
-
- Andersen E. C., Lu X., Horvitz H. R., 2006. C. elegans ISWI and NURF301 antagonize an Rb-like pathway in the determination of multiple cell fates. Development 133: 2695–2704. - PubMed
-
- Baugh L. R., Sternberg P. W., 2006. DAF-16/FOXO regulates transcription of cki-1/Cip/Kip and repression of lin-4 during C. elegans L1 arrest. Curr. Biol. 16: 780–785. - PubMed
-
- Bender L. B., Cao R., Zhang Y., Strome S., 2004. The MES-2/MES-3/MES-6 complex and regulation of histone H3 methylation in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 14: 1639–1643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
