Hypoxia-inducible factors: coupling glucose metabolism and redox regulation with induction of the breast cancer stem cell phenotype
- PMID: 28007895
- PMCID: PMC5286373
- DOI: 10.15252/embj.201695204
Hypoxia-inducible factors: coupling glucose metabolism and redox regulation with induction of the breast cancer stem cell phenotype
Abstract
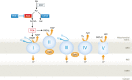
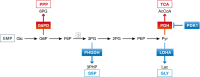
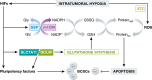
Reduced oxygen availability (hypoxia) leads to increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by the electron transport chain. Here, I review recent work delineating mechanisms by which hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) mediates adaptive metabolic responses to hypoxia, including increased flux through the glycolytic pathway and decreased flux through the tricarboxylic acid cycle, in order to decrease mitochondrial ROS production. HIF-1 also mediates increased flux through the serine synthesis pathway and mitochondrial one-carbon (folate cycle) metabolism to increase mitochondrial antioxidant production (NADPH and glutathione). Dynamic maintenance of ROS homeostasis is required for induction of the breast cancer stem cell phenotype in response to hypoxia or cytotoxic chemotherapy. Consistently, inhibition of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase, the first enzyme of the serine synthesis pathway, in breast cancer cells impairs tumor initiation, metastasis, and response to cytotoxic chemotherapy. I discuss how these findings have important implications for understanding the logic of the tumor microenvironment and for improving therapeutic responses in women with breast cancer.
Keywords: cancer; one‐carbon metabolism; pluripotency; progression; serine synthesis.
© 2016 The Author.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of cancer cell metabolism by hypoxia-inducible factor 1.Semin Cancer Biol. 2009 Feb;19(1):12-6. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.11.009. Epub 2008 Dec 9. Semin Cancer Biol. 2009. PMID: 19114105 Review.
-
Resveratrol suppresses cancer cell glucose uptake by targeting reactive oxygen species-mediated hypoxia-inducible factor-1α activation.J Nucl Med. 2013 Dec;54(12):2161-7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.115436. Epub 2013 Nov 12. J Nucl Med. 2013. PMID: 24221993
-
Hypoxia inducible factors as mediators of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species homeostasis in physiological normoxia.Med Hypotheses. 2019 Aug;129:109249. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2019.109249. Epub 2019 May 27. Med Hypotheses. 2019. PMID: 31371070
-
Tumor microenvironment and metabolic synergy in breast cancers: critical importance of mitochondrial fuels and function.Semin Oncol. 2014 Apr;41(2):195-216. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2014.03.002. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Semin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24787293 Review.
-
Theileria induces oxidative stress and HIF1α activation that are essential for host leukocyte transformation.Oncogene. 2014 Apr 3;33(14):1809-17. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.134. Epub 2013 May 13. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23665677
Cited by
-
Hypoxia and HIF Signaling: One Axis with Divergent Effects.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 5;21(16):5611. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165611. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32764403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyamine Anabolism Promotes Chemotherapy-Induced Breast Cancer Stem Cell Enrichment.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Oct;11(40):e2404853. doi: 10.1002/advs.202404853. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39058337 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Classification and Intervention Opportunities for Tumor Energy Dysfunction.Metabolites. 2021 Apr 23;11(5):264. doi: 10.3390/metabo11050264. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 33922558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIF‑1α in myocardial ischemia‑reperfusion injury (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2021 May;23(5):352. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.11991. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33760122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pemetrexed Hinders Translation Inhibition upon Low Glucose in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Metabolites. 2021 Mar 26;11(4):198. doi: 10.3390/metabo11040198. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 33810430 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

