Interacting post-muscarinic receptor signaling pathways potentiate matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression and invasion of human colon cancer cells
- PMID: 28008134
- PMCID: PMC5650067
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20160704
Interacting post-muscarinic receptor signaling pathways potentiate matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression and invasion of human colon cancer cells
Abstract
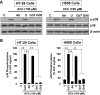
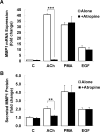
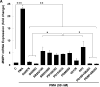
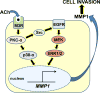
M3 muscarinic receptor (M3R) expression is increased in colon cancer; M3R activation stimulates colon cancer cell invasion via cross-talk with epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR), post-EGFR activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), and induction of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP1) expression. MMP1 expression is strongly associated with tumor metastasis and adverse outcomes. Here, we asked whether other MAPKs regulate M3R agonist-induced MMP1 expression. In addition to activating ERK1/2, we found that treating colon cancer cells with acetylcholine (ACh) stimulated robust time- and dose-dependent phosphorylation of p38 MAPK. Unlike ERK1/2 activation, ACh-induced p38 phosphorylation was EGFR-independent and blocked by inhibiting protein kinase C-α (PKC-α). Inhibiting activation of PKC-α, EGFR, ERK1/2, or p38-α/β alone attenuated, but did not abolish ACh-induced MMP1 expression, a finding that predicted potentiating interactions between these pathways. Indeed, ACh-induced MMP1 expression was abolished by incubating cells with either an EGFR or MEK/ERK1/2 inhibitor combined with a p38-α/β inhibitor. Activating PKC-α and EGFR directly with the combination of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and EGF potentiated MMP1 gene and protein expression, and cell invasion. PMA- and ACh-induced MMP1 expression were strongly diminished by inhibiting Src and abolished by concurrently inhibiting both p38-α/β and Src, indicating that Src mediates the cross-talk between PKC-α and EGFR signaling. Using siRNA knockdown, we identified p38-α as the relevant p38 isoform. Collectively, these studies uncover novel functional interactions between post-muscarinic receptor signaling pathways that augment MMP1 expression and drive colon cancer cell invasion; targeting these potentiating interactions has therapeutic potential.
Keywords: cell invasion; cell signaling; colorectal cancer; matrix metalloproteinases; muscarinic receptors; p38 MAPK.
© 2017 The Author(s); published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Figures
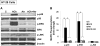
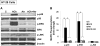












References
-
- Kohler BA, Sherman RL, Howlader N, Jemal A, Ryerson AB, Henry KA, Boscoe FP, Cronin KA, Lake A, Noone AM, Henley SJ, Eheman CR, Anderson RN, Penberthy L. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, 1975–2011, Featuring Incidence of Breast Cancer Subtypes by Race/Ethnicity, Poverty, and State. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107 djv048. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hayat MJ, Howlader N, Reichman ME, Edwards BK. Cancer statistics, trends, and multiple primary cancer analyses from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. Oncologist. 2007;12:20–37. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

