Chemoresistance and targeted therapies in ovarian and endometrial cancers
- PMID: 28008141
- PMCID: PMC5354810
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14021
Chemoresistance and targeted therapies in ovarian and endometrial cancers
Abstract
Gynecological cancers are known for being very aggressive at their advanced stages. Indeed, the survival rate of both ovarian and endometrial cancers is very low when diagnosed lately and the success rate of current chemotherapy regimens is not very efficient. One of the main reasons for this low success rate is the acquired chemoresistance of these cancers during their progression. The mechanisms responsible for this acquired chemoresistance are numerous, including efflux pumps, repair mechanisms, survival pathways (PI3K/AKT, MAPK, EGFR, mTOR, estrogen signaling) and tumor suppressors (P53 and Par-4). To overcome these resistances, a new type of therapy has emerged named targeted therapy. The principle of targeted therapy is simple, taking advantage of changes acquired in malignant cancer cells (receptors, proteins, mechanisms) by using compounds specifically targeting these, thus limiting their action on healthy cells. Targeted therapies are emerging and many clinical trials targeting these pathways, frequently involved in chemoresistance, have been tested on gynecological cancers. Despite some targets being less efficient than expected as mono-therapies, the combination of compounds seems to be the promising avenue. For instance, we demonstrate using ChIP-seq analysis that estrogen downregulate tumor suppressor Par-4 in hormone-dependent cells by directly binding to its DNA regulatory elements and inhibiting estrogen signaling could reinstate Par-4 apoptosis-inducing abilities. This review will focus on the chemoresistance mechanisms and the clinical trials of targeted therapies associated with these, specifically for endometrial and ovarian cancers.
Keywords: PI3K; chemoresistance; estrogen; gynecological cancers; targeted therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
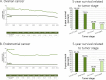
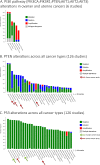
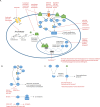

References
-
- Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JWW, Comber H, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 countries in 2012. European Journal of Cancer. 2013;49:1374–403. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2012.12.027 - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2015.
-
- Canadian Cancer . Canadian Cancer Statistics. Canadian Cancer Society; Toronto, ON: 2015. Society’s Advisory Committee on Cancer Statistics.
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Casciato DA, Territo MC. Manual of clinical oncology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.; 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

