Advances in islet encapsulation technologies
- PMID: 28008169
- PMCID: PMC11286215
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd.2016.232
Advances in islet encapsulation technologies
Erratum in
-
Advances in islet encapsulation technologies.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017 Apr 28;16(5):367. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.67. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 28450719 No abstract available.
Abstract
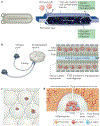
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing islet cells of the pancreas. Although islet transplantation has proved to be successful for some patients with type 1 diabetes, its widespread use is limited by islet donor shortage and the requirement for lifelong immunosuppression. An encapsulation strategy that can prevent the rejection of xenogeneic islets or of stem cell-derived allogeneic islets can potentially eliminate both of these barriers. Although encapsulation technology has met several challenges, the convergence of expertise in materials, nanotechnology, stem cell biology and immunology is allowing us to get closer to the goal of encapsulated islet cell therapy for humans.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diabetes report card 2014. CDC; http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/library/diabetesreportcard2014.pdf (2015).
-
- National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. National diabetes statistics report, 2014: estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States. CDC; http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/statsreport14/national-diabetes-report-... (2014).
-
- Ryan EA et al. Five-year follow-up after clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes 54, 2060–2069 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Shapiro AM et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N. Engl. J. Med 343, 230–238 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

