Transbuccal delivery of betahistine dihydrochloride from mucoadhesive tablets with a unidirectional drug flow: in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo evaluation
- PMID: 28008227
- PMCID: PMC5167456
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S120613
Transbuccal delivery of betahistine dihydrochloride from mucoadhesive tablets with a unidirectional drug flow: in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo evaluation
Abstract
Objective: Betahistine dihydrochloride (BH.2HCl), an anti-vertigo histamine analog used in the treatment of Ménière's disease, undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism and suffers from short biological half-life. The aim of the present work was to develop and estimate controlled release mucoadhesive buccal tablets of BH.2HCl with a unidirectional drug flow to overcome this encumbrance.
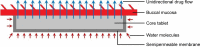
Methods: A direct compression method was adopted for preparation of the tablets using mucoadhesive polymers like guar gum, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose K4M, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and their combinations. The tablets were coated from all surfaces except one surface with a solution of 5% (w/v) cellulose acetate and 1% (w/v) dibutyl phthalate. Different permeation enhancers like 2% sodium deoxycholate, 2% sodium cholate hydrate (SCH) and 5% menthol were tested. Swelling index, ex vivo residence time, mucoadhesion strength, in vivo testing of mucoadhesion time, in vitro dissolution and ex vivo permeation were carried out. Furthermore, compatibility and accelerated stability studies were performed for the drug excipients. Finally, drug bioavailability of the BH.2HCl-optimized buccal mucoadhesive formulation was compared with that of the orally administered Betaserc® 24 mg tablet in six healthy male volunteers.
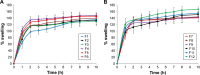
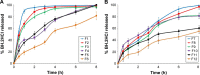
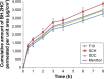
Results: Formulation F10, which contained a combination of 35% guar gum and 5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, exhibited long adhesion time, high adhesion strength and diminished irritation to volunteers and showed zero-order release kinetics. SCH produced a significant enhancement in permeation of BH.2HCl across buccal mucosa. BH.2HCl-optimized buccal mucoadhesive formulation showed percentage relative bioavailability of 177%.
Conclusion: The developed mucoadhesive tablets represent a promising alternative for the buccal delivery of BH.2HCl.
Keywords: betahistine dihydrochloride; permeation enhancer; relative bioavailability; transbuccal delivery; unidirectional drug flow.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
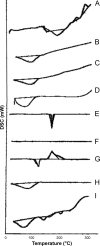
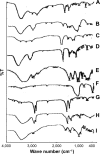
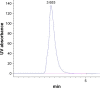


Similar articles
-
Enhanced bioavailability of buspirone hydrochloride via cup and core buccal tablets: formulation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation.Int J Pharm. 2014 Mar 10;463(1):68-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Int J Pharm. 2014. PMID: 24412520 Clinical Trial.
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of locust bean gum and chitosan combination as a carrier for buccal drug delivery.Pharmazie. 2008 May;63(5):342-7. Pharmazie. 2008. PMID: 18557416
-
Badam gum: a natural polymer in mucoadhesive drug delivery. Design, optimization, and biopharmaceutical evaluation of badam gum-based metoprolol succinate buccoadhesive tablets.Drug Deliv. 2016;23(1):195-206. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.908979. Epub 2014 May 14. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 24825493
-
Recent advances in guar gum based drug delivery systems and their administrative routes.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jun 30;181:653-671. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.087. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33766594 Review.
-
Drug delivery from the oral cavity: a focus on mucoadhesive buccal drug delivery systems.PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2012 Sep-Oct;66(5):466-500. doi: 10.5731/pdajpst.2012.00877. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2012. PMID: 23035030 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Approaches for Sublingual and Buccal Administration.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 5;10:1328. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01328. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31827435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabrication and appraisal of axitinib loaded PEGylated spanlastics against MCF- 7 and OV- 2774 cell lines using molecular docking methods and in-vitro study.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 1;20(7):e0325055. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325055. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40591624 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Mucoadhesive Vehicle Based on Lyophilized Liposomes for Drug Delivery through the Sublingual Mucosa.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jul 19;14(7):1497. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071497. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890395 Free PMC article.
-
Tailoring of Selenium-Plated Novasomes for Fine-Tuning Pharmacokinetic and Tumor Uptake of Quercetin: In Vitro Optimization and In Vivo Radiobiodistribution Assessment in Ehrlich Tumor-Bearing Mice.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Apr 16;14(4):875. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040875. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35456709 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing Spanlastics for Improving the Ocular Delivery of Clotrimazole: In vitro Characterization, Ex vivo Permeability, Microbiological Assessment and In vivo Safety Study.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Sep 10;16:6249-6261. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S319348. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34531656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosen T. Pragmatic and profound benefits of acyclovir buccal adhesive tablets. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15(6):775–777. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

