A genetic screen of the mutations in the Korean patients with early-onset Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 28008242
- PMCID: PMC5167483
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S116724
A genetic screen of the mutations in the Korean patients with early-onset Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
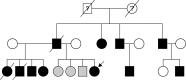
Early-onset Alzheimer's disease (EOAD) has distinct clinical characteristics in comparison to late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD). The genetic contribution is suggested to be more potent in EOAD. However, the frequency of causative mutations in EOAD could be variable depending on studies. Moreover, no mutation screening study has been performed yet employing large population in Korea. Previously, we reported that the rate of family history of dementia in EOAD patients was 18.7% in a nationwide hospital-based cohort study, the Clinical Research Center for Dementia of South Korea (CREDOS) study. This rate is much lower than in other countries and is even comparable to the frequency of LOAD patients in our country. To understand the genetic characteristics of EOAD in Korea, we screened the common Alzheimer's disease (AD) mutations in the consecutive EOAD subjects from the CREDOS study from April 2012 to February 2014. We checked the sequence of APP (exons 16-17), PSEN1 (exons 3-12), and PSEN2 (exons 3-12) genes. We identified different causative or probable pathogenic AD mutations, PSEN1 T116I, PSEN1 L226F, and PSEN2 V214L, employing 24 EOAD subjects with a family history and 80 without a family history of dementia. PSEN1 T116I case demonstrated autosomal dominant trait of inheritance, with at least 11 affected individuals over 2 generations. However, there was no family history of dementia within first-degree relation in PSEN1 L226F and PSEN2 V214L cases. Approximately, 55.7% of the EOAD subjects had APOE ε4 allele, while none of the mutation-carrying subjects had the allele. The frequency of genetic mutation in this study is lower compared to the studies from other countries. The study design that was based on nationwide cohort, which minimizes selection bias, is thought to be one of the contributors to the lower frequency of genetic mutation. However, the possibility of the greater likeliness of earlier onset of sporadic AD in Korea cannot be excluded. We suggest early AD onset and not carrying APOE ε4 allele are more reliable factors for predicting an induced genetic mutation than the presence of the family history in Korean EOAD population.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; apolipoprotein-E; early onset Alzheimer’s disease; genetics; mutation; presenilin; sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 Mutations in Asian Patients with Early-Onset Alzheimer Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 25;20(19):4757. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194757. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31557888 Free PMC article.
-
Gene mutations in a Han Chinese Alzheimer's disease cohort.Brain Behav. 2019 Jan;9(1):e01180. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1180. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 30549411 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Genetics of Early- and Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Gene Ther. 2021;21(1):43-52. doi: 10.2174/1566523220666201123112822. Curr Gene Ther. 2021. PMID: 33231156 Review.
-
Mutations, associated with early-onset Alzheimer's disease, discovered in Asian countries.Clin Interv Aging. 2016 Oct 17;11:1467-1488. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S116218. eCollection 2016. Clin Interv Aging. 2016. PMID: 27799753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 mutations in early-onset Alzheimer disease: A genetic screening study of familial and sporadic cases.PLoS Med. 2017 Mar 28;14(3):e1002270. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002270. eCollection 2017 Mar. PLoS Med. 2017. PMID: 28350801 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of variants in PSEN1, PSEN2, and APP genes in Chinese patients with early-onset Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Feb 27;17(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01702-0. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40016812 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and genetic characteristics in a central-southern Chinese cohort of early-onset Alzheimer's disease.Front Neurol. 2023 Mar 27;14:1119326. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1119326. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37051054 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance of Early-Onset Alzheimer's Mutations in Asian and Western Populations: A Scoping Review.Genes (Basel). 2025 Mar 17;16(3):345. doi: 10.3390/genes16030345. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149496 Free PMC article.
-
APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 Variants in Alzheimer's Disease: Systematic Re-evaluation According to ACMG Guidelines.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jun 18;13:695808. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.695808. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34220489 Free PMC article.
-
PSEN2 and ABCA7 variants causing early-onset preclinical pathological changes in Alzheimer's disease: a case report and literature review.Neurol Sci. 2023 Jun;44(6):1987-2001. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06602-5. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36701017 Review.
References
-
- Panegyres PK, Chen HY, Coalition against major diseases (CAMD) Early-onset Alzheimer’s disease: a global cross-sectional analysis. Eur J Neurol. 2014;21(9):1149–1154. - PubMed
-
- Cho H, Jeon S, Kang SJ, et al. Longitudinal changes of cortical thickness in early- versus late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2013;34(7):1921.e9–1921.e15. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

