Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors among workers at a private tertiary center in Angola
- PMID: 28008265
- PMCID: PMC5167297
- DOI: 10.2147/VHRM.S120735
Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors among workers at a private tertiary center in Angola
Abstract
Background: The burden of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) is increasing in most countries of sub-Saharan Africa. However, as there is a scarcity of data, little is known about CVD in Angola. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of prehypertension, hypertension, prediabetes, diabetes, overweight, and obesity among workers at a private tertiary center in Angola.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among 781 workers of Clínica Girassol, a tertiary health care center in Angola, during the month of November 2013. Demographic, anthropometric, and clinical variables were analyzed.
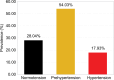
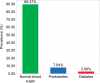
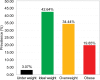
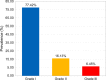
Results: Of the 781 participants studied, 50.44% were males and 78.11% were under 40 years old. The prevalence of hypertension and prehypertension was 17.93% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 15.24%-20.74%) and 54.03% (95% CI: 50.58%-57.62%), respectively. Among hypertensive subjects, 83.57% (117) were unaware of the diagnosis. Hypertension was associated with age (≥40 years) (odds ratio [OR]: 6.21; 95% CI: 4.18-9.24; P<0.001) and with overweight and obesity (OR: 2.32; 95% CI: 1.56-3.44; P<0.001). The prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes was 2.69% (95% CI: 1.54%-3.97%) and 7.94% (95% CI: 6.02%-9.99%), respectively. The prevalence of overweight was 34.44% (95% CI: 31.11%-37.90%) and 19.85% (95% CI: 17.03%-22.79%) for obesity. There was an association between overweight and obesity and the female sex (OR: 1.71; 95% CI: 1.29-2.28; P<0.001). The prevalence of family history of CVD, smoking, and alcoholism was 52.24%, 4.87%, and 45.33%, respectively.
Conclusion: There was a high prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in apparently healthy workers at the private tertiary center in Angola.
Keywords: Angola; diabetes mellitus; hypertension; obesity; prehypertension; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2010. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010.
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217–223. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

