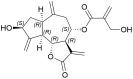
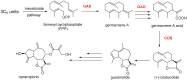
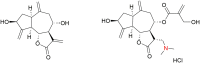Cynaropicrin: A Comprehensive Research Review and Therapeutic Potential As an Anti-Hepatitis C Virus Agent
- PMID: 28008316
- PMCID: PMC5143615
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00472
Cynaropicrin: A Comprehensive Research Review and Therapeutic Potential As an Anti-Hepatitis C Virus Agent
Abstract
The different pharmacologic properties of plants-containing cynaropicrin, especially artichokes, have been known for many centuries. More recently, cynaropicrin exhibited a potential activity against all genotypes of hepatitis C virus (HCV). Cynaropicrin has also shown a wide range of other pharmacologic properties such as anti-hyperlipidemic, anti-trypanosomal, anti-malarial, antifeedant, antispasmodic, anti-photoaging, and anti-tumor action, as well as activation of bitter sensory receptors, and anti-inflammatory properties (e.g., associated with the suppression of the key pro-inflammatory NF-κB pathway). These pharmacological effects are very supportive factors to its outstanding activity against HCV. Structurally, cynaropicrin might be considered as a potential drug candidate, since it has no violations for the rule of five and its water-solubility could allow formulation as therapeutic injections. Moreover, cynaropicrin is a small molecule that can be easily synthesized and as the major constituent of the edible plant artichoke, which has a history of safe dietary use. In summary, cynaropicrin is a promising bioactive natural product that, with minor hit-to-lead optimization, might be developed as a drug for HCV.
Keywords: anti-gastritis action; anti-hepatitis C virus; anti-hyperlipidemic; anti-inflammatory; anti-parasite; antibacterial; antitumor; cynaropicrin.
Figures
References
-
- Adekenova A. S., Sakenova P. Y., Ivasenko S. A., Khabarov I. A., Adekenov S. M., Berthod A. (2015). Gram-scale purification of two sesquiterpene lactones from chartolepsis intermedia boiss. Chromatographia 79, 37–43. 10.1007/s10337-015-3000-1 - DOI
-
- Ahmed A., Jakupovic J., Seif A. A., El-Ela M. A., El-Ghazouly M. (1990). A guaianolide from Amberboa tubuliflora. Phytochemistry 29, 3946–3947. 10.1016/0031-9422(90)85370-U - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials