R-Type Ca2+ channels couple to inhibitory neurotransmission to the longitudinal muscle in the guinea-pig ileum
- PMID: 28008669
- PMCID: PMC5332280
- DOI: 10.1113/EP086027
R-Type Ca2+ channels couple to inhibitory neurotransmission to the longitudinal muscle in the guinea-pig ileum
Abstract
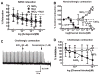
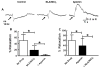
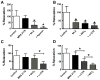
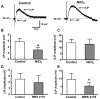
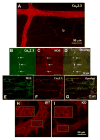
What is the central question of this study? Subtypes of enteric neurons are coded by the neurotransmitters they synthesize, but it is not known whether enteric neuron subtypes might also be coded by other proteins, including calcium channel subtypes controlling neurotransmitter release. What is the main finding and its importance? Our data indicate that guinea-pig ileum myenteric neuron subtypes may be coded by calcium channel subtypes. We found that R-type calcium channels are expressed by inhibitory but not excitatory longitudinal muscle motoneurons. R-Type calcium channels are also not expressed by circular muscle inhibitory motoneurons. Calcium channel subtype-selective antagonists could be used to target subtypes of neurons to treat gastrointestinal motility disorders. There is evidence that R-type Ca2+ channels contribute to synaptic transmission in the myenteric plexus. It is unknown whether R-type Ca2+ channels contribute to neuromuscular transmission. We measured the effects of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor nitro-l-arginine (NLA), Ca2+ channel blockers and apamin (SK channel blocker) on neurogenic relaxations and contractions of the guinea-pig ileum longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus (LMMP) in vitro. We used intracellular recordings to measure inhibitory junction potentials. Immunohistochemical techniques localized R-type Ca2+ channel protein in the LMMP and circular muscle. Cadmium chloride (pan-Ca2+ channel blocker) blocked and NLA and NiCl2 (R-type Ca2+ channel blocker) reduced neurogenic relaxations in a non-additive manner. Nickel chloride did not alter neurogenic cholinergic contractions, but it potentiated neurogenic non-cholinergic contractions. Relaxations were inhibited by apamin, NiCl2 and NLA and were blocked by combined application of these drugs. Relaxations were reduced by NiCl2 or ω-conotoxin (N-type Ca2+ channel blocker) and were blocked by combined application of these drugs. Longitudinal muscle inhibitory junction potentials were inhibited by NiCl2 but not MRS 2179 (P2Y1 receptor antagonist). Circular muscle inhibitory junction potentials were blocked by apamin, MRS 2179, ω-conotoxin and CdCl2 but not NiCl2 . We conclude that neuronal R-type Ca2+ channels contribute to inhibitory neurotransmission to longitudinal muscle but less so or not all in the circular muscle of the guinea-pig ileum.
Keywords: calcium channel; nitric oxide; purinergic signaling; synaptic transmission.
© 2016 The Authors. Experimental Physiology © 2016 The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts to disclose.
Figures
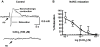
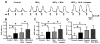
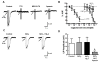
Similar articles
-
R-type Ca(2+) channels contribute to fast synaptic excitation and action potentials in subsets of myenteric neurons in the guinea pig intestine.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010 Dec;22(12):e353-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2010.01596.x. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010. PMID: 20879993
-
Endogenous NO inhibits NANC but not cholinergic neurotransmission to circular muscle of guinea pig ileum.Am J Physiol. 1996 Nov;271(5 Pt 1):G904-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1996.271.5.G904. Am J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8944706
-
Inhibitory neuromuscular transmission mediated by the P2Y1 purinergic receptor in guinea pig small intestine.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):G1483-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00450.2006. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17322065
-
Enteric Inhibitory Neurotransmission, Starting Down Under.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;891:21-9. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-27592-5_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27379631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal nitric oxide in the gut.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1993 Nov-Dec;8(6):590-603. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1993.tb01658.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1993. PMID: 7506586 Review.
Cited by
-
New Insights Into Interactions of Presynaptic Calcium Channel Subtypes and SNARE Proteins in Neurotransmitter Release.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Jul 16;11:213. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00213. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30061813 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotransmitters responsible for purinergic motor neurotransmission and regulation of GI motility.Auton Neurosci. 2021 Sep;234:102829. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2021.102829. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Auton Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34146957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baurand A, Raboisson P, Freund M, Léon C, Cazenave JP, Bourguignon JJ, Gachet C. Inhibition of platelet function by administration of MRS2179, a P2Y1 receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001;412:213–221. - PubMed
-
- Benko R, Undi S, Wolf M, Vereczkei A, Illenyi L, Kassai M, Cseke L, Kelemen D, Horvath OP, Antal A, Magyar K, Bartho L. P2 purinoceptor antagonists inhibit the non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic relaxation of the human colon in vitro. Neuroscience. 2007;147:146–152. - PubMed
-
- Bian X, Zhou X, Galligan JJ. R-type calcium channels in myenteric neurons of guinea pig small intestine. Am J Physiol. 2004;287:G134–142. - PubMed
-
- Bkaily G, Avedanian L, Al-Khoury J, Chamoun M, Semaan R, Jubinville-Leblanc C, D’Orléans-Juste P, Jacques D. Nuclear membrane R-type calcium channels mediate cytosolic ET-1-induced increase of nuclear calcium in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015;93:291–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

