Basal Serum Neurokinin B Levels in Differentiating Idiopathic Central Precocious Puberty from Premature Thelarche
- PMID: 28008860
- PMCID: PMC5463280
- DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.3817
Basal Serum Neurokinin B Levels in Differentiating Idiopathic Central Precocious Puberty from Premature Thelarche
Abstract
Objective: To find out the diagnostic role of kisspeptin and neurokinin B in idiopathic central precocious puberty (ICPP) and premature thelarche (PT).
Methods: The girls who presented with early breast development before the age of 8 years were evaluated. Patients with intracranial pathologies were excluded. Basal and stimulated follicle-stimulating hormone/luteinizing hormone (LH) levels and basal neurokinin B/kisspeptin levels were measured. Patients who had peak value of LH >5 mIU/mL and a bone age (BA)/chronological age (CA) ratio >1.1 were diagnosed as central precocious puberty (CPP), while cases who did not meet these criteria were diagnosed as PT. Healthy age-matched prepubertal girls were included as the control group.
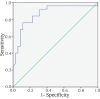
Results: The study group contained 25 girls with ICPP (7±0.8 years), 35 girls with PT (6.8±0.7 years), and 30 controls (6.7±0.7 years). Basal serum kisspeptin and neurokinin B levels were 2.36±0.47 ng/mL and 2.61±0.32 ng/mL, respectively in the ICPP group, 2.23±0.43 ng/mL and 2.24±0.23 ng/mL, respectively in the PT group, and 1.92±0.33 ng/mL and 2.03±0.24 ng/mL, respectively in the controls. Both kisspeptin and neurokinin B levels were higher in the ICPP and PT groups compared to controls (p<0.05). Moreover, basal neurokinin B level was different between ICPP and PT groups (p<0.01). A serum neurokinin B level of 2.42 ng/mL provided the most appropriate level to differentiate ICPP from PT, with a sensitivity of 84% and specificity of 77.1%.
Conclusion: Differentiation of CPP from PT is sometime difficult, and there is a need for a simple method for the differential diagnosis. Our results suggest that basal serum neurokinin B level can be used as an adjunctive parameter to differentiate ICCP from PT.
Keywords: Neurokinin B; kisspeptin precocious puberty..
Figures
Similar articles
-
Significance of serum neurokinin B and kisspeptin levels in the differential diagnosis of premature thelarche and idiopathic central precocious puberty.Peptides. 2015 Feb;64:29-33. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2014.12.011. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Peptides. 2015. PMID: 25572302
-
Serum kisspeptin, neurokinin B and inhibin B levels can be used as alternative parameters to distinguish idiopathic CPP from premature thelarche in the early stages of puberty.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2023 Jun;98(6):788-795. doi: 10.1111/cen.14906. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2023. PMID: 36879296
-
Premature thelarche and central precocious puberty: the relationship between clinical presentation and the gonadotropin response to luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Sep;67(3):474-9. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-3-474. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988. PMID: 3137242
-
Kisspeptin Levels in Girls with Precocious Puberty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Horm Res Paediatr. 2020;93(11-12):589-598. doi: 10.1159/000515660. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Horm Res Paediatr. 2020. PMID: 33887744
-
Dose inhibin B or anti-Müllerian hormone relate to precocious puberty in girls? result of a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Ovarian Res. 2023 Nov 23;16(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01302-2. J Ovarian Res. 2023. PMID: 37996919 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Premature Thelarche: An Updated Review.Curr Pediatr Rev. 2024;20(4):500-509. doi: 10.2174/1573396320666230726110658. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2024. PMID: 37496240 Review.
-
The role of kisspeptin and MKRN3 in the diagnosis of central precocious puberty in girls.Endocr Connect. 2021 Sep 20;10(9):1147-1154. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0182. Endocr Connect. 2021. PMID: 34414898 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
