The Specific Protein Kinase R (PKR) Inhibitor C16 Protects Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Brain Damages by Inhibiting Neuroinflammation in a Neonatal Rat Model
- PMID: 28008894
- PMCID: PMC5207129
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.898139
The Specific Protein Kinase R (PKR) Inhibitor C16 Protects Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Brain Damages by Inhibiting Neuroinflammation in a Neonatal Rat Model
Abstract
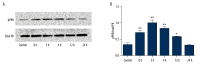
BACKGROUND Brain injuries induced by hypoxia-ischemia in neonates contribute to increased mortality and lifelong neurological dysfunction. The specific PKR inhibitor C16 has been previously demonstrated to exert a neuroprotective role in adult brain injuries. However, there is no recent study available concerning its protective role in hypoxia-ischemia-induced immature brain damage. Therefore, we investigated whether C16 protects against neonatal hypoxia-ischemia injuries in a neonatal rat model. MATERIAL AND METHODS Postnatal day 7 (P7) rats were used to establish classical hypoxia-ischemia animal models, and C16 postconditioning with 100 ug/kg was performed immediately after hypoxia. Western blot analysis was performed to quantify the phosphorylation of the PKR at 0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, and phosphorylation of NF-κB 24h after hypoxia exposure. The TTC stain for infarction area and TUNEL stain for apoptotic cells were assayed 24 h after the brain hypoxia. Gene expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α was performed at 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h. RESULTS The level of PKR autophosphorylation was increased dramatically, especially at 3 h (C16 group vs. HI group, P<0.01). Intraperitoneal C16 administration reduced the infarct volume and apoptosis ratio after this insult (C16 group vs. HI group<0.01), and C16 reduced proinflammatory cytokines mRNA expression, partly through inhibiting NF-κB activation (C16 group vs. HI group<0.05). CONCLUSIONS C16 can protect immature rats against hypoxia-ischemia-induced brain damage by modulating neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Carnosine pretreatment protects against hypoxia-ischemia brain damage in the neonatal rat model.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep 30;667(1-3):202-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.06.003. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21693116
-
Inhibition of Protein Kinase R by C16 Protects the Retinal Ganglion Cells from Hypoxia-induced Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis.Curr Eye Res. 2021 May;46(5):719-730. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1826980. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Curr Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33026257
-
The specific PKR inhibitor C16 prevents apoptosis and IL-1β production in an acute excitotoxic rat model with a neuroinflammatory component.Neurochem Int. 2014 Jan;64:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.10.012. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24211709
-
Resveratrol and Some of Its Derivatives as Promising Prophylactic Treatments for Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 14;14(18):3793. doi: 10.3390/nu14183793. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36145168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury in the term infant: current concepts.Clin Perinatol. 2002 Dec;29(4):585-602, v. doi: 10.1016/s0095-5108(02)00059-3. Clin Perinatol. 2002. PMID: 12516737 Review.
Cited by
-
PACT-mediated PKR activation acts as a hyperosmotic stress intensity sensor weakening osmoadaptation and enhancing inflammation.Elife. 2020 Mar 16;9:e52241. doi: 10.7554/eLife.52241. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32175843 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase R regulates pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression by modulating the cell cycle via GADD45A.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 10;15(1):24966. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06213-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40640279 Free PMC article.
-
Exocyst protein subnetworks integrate Hippo and mTOR signaling to promote virus detection and cancer.Cell Rep. 2021 Aug 3;36(5):109491. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109491. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34348154 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine Ameliorates MCAO Induced Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Activation of the BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2018 Mar;43(3):702-710. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2472-4. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29357017
-
A tale of two proteins: PACT and PKR and their roles in inflammation.FEBS J. 2021 Nov;288(22):6365-6391. doi: 10.1111/febs.15691. Epub 2021 Jan 15. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 33387379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vannucci RC, Connor JR, Mauger DT, et al. Rat model of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. J Neurosci Res. 1999;55(2):158–63. - PubMed
-
- Ferriero DM. Neonatal brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(19):1985–95. - PubMed
-
- Nelson KB, Lynch JK. Stroke in newborn infants. Lancet Neurol. 2004;3(3):150–58. - PubMed
-
- Zhao P, Zuo Z. Isoflurane preconditioning induces neuroprotection that is inducible nitric oxide synthase-dependent in neonatal rats. Anesthesiology. 2004;101(3):695–703. - PubMed
-
- Payton KS, Sheldon RA, Mack DW, et al. Antioxidant status alters levels of Fas-associated death domain-like IL-1β-converting enzyme inhibitory protein following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Dev Neurosci. 2007;29(4–5):403–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

