Drosophila microRNA-34 Impairs Axon Pruning of Mushroom Body γ Neurons by Downregulating the Expression of Ecdysone Receptor
- PMID: 28008974
- PMCID: PMC5180235
- DOI: 10.1038/srep39141
Drosophila microRNA-34 Impairs Axon Pruning of Mushroom Body γ Neurons by Downregulating the Expression of Ecdysone Receptor
Abstract
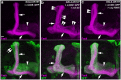
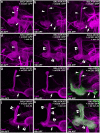
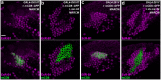
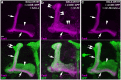
MicroRNA-34 (miR-34) is crucial for preventing chronic large-scale neurite degeneration in the aged brain of Drosophila melanogaster. Here we investigated the role of miR-34 in two other types of large-scale axon degeneration in Drosophila: axotomy-induced axon degeneration in olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) and developmentally related axon pruning in mushroom body (MB) neurons. Ectopically overexpressed miR-34 did not inhibit axon degeneration in OSNs following axotomy, whereas ectopically overexpressed miR-34 in differentiated MB neurons impaired γ axon pruning. Intriguingly, the miR-34-induced γ axon pruning defect resulted from downregulating the expression of ecdysone receptor B1 (EcR-B1) in differentiated MB γ neurons. Notably, the separate overexpression of EcR-B1 or a transforming growth factor- β receptor Baboon, whose activation can upregulate the EcR-B1 expression, in MB neurons rescued the miR-34-induced γ axon pruning phenotype. Future investigations of miR-34 targets that regulate the expression of EcR-B1 in MB γ neurons are warranted to elucidate pathways that regulate axon pruning, and to provide insight into mechanisms that control large-scale axon degeneration in the nervous system.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genomic analysis of Drosophila neuronal remodeling: a role for the RNA-binding protein Boule as a negative regulator of axon pruning.J Neurosci. 2008 Jun 11;28(24):6092-103. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0677-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18550751 Free PMC article.
-
Mushroom body neuronal remodelling is necessary for short-term but not for long-term courtship memory in Drosophila.Eur J Neurosci. 2012 Jun;35(11):1684-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08103.x. Epub 2012 May 9. Eur J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22571719
-
piggyBac-based mosaic screen identifies a postmitotic function for cohesin in regulating developmental axon pruning.Dev Cell. 2008 Feb;14(2):227-38. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.11.001. Dev Cell. 2008. PMID: 18267091 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptors and Drosophila neuronal remodeling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Feb;1849(2):187-95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.05.024. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 24882358 Review.
-
Spatiotemporal regulation of developmental neurite pruning: Molecular and cellular insights from Drosophila models.Neurosci Res. 2021 Jun;167:54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2020.11.010. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Neurosci Res. 2021. PMID: 33309868 Review.
Cited by
-
Individual components of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex have distinct roles in memory neurons of the Drosophila mushroom body.Dis Model Mech. 2019 Mar 25;12(3):dmm037325. doi: 10.1242/dmm.037325. Dis Model Mech. 2019. PMID: 30923190 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of Endogenous Type I TGF-β Receptor Baboon in the Drosophila Brain.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 20;10(1):5132. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61950-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32198477 Free PMC article.
-
Distal Axonal Proteins and Their Related MiRNAs in Cultured Cortical Neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Apr;56(4):2703-2713. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1266-7. Epub 2018 Jul 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30054858 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb group genes are required for neuronal pruning in Drosophila.BMC Biol. 2023 Feb 15;21(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12915-023-01534-0. BMC Biol. 2023. PMID: 36793038 Free PMC article.
-
ame-miR-34 Modulates the Larval Body Weight and Immune Response of Apis mellifera Workers to Ascosphara apis Invasion.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 7;24(2):1214. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021214. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kandel E. R. Principles of neural science. 5th edn, (McGraw-Hill, 2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

