Down-regulation of common NFκB-iNOS pathway by chronic Thalidomide treatment improves Hepatopulmonary Syndrome and Muscle Wasting in rats with Biliary Cirrhosis
- PMID: 28009008
- PMCID: PMC5180197
- DOI: 10.1038/srep39405
Down-regulation of common NFκB-iNOS pathway by chronic Thalidomide treatment improves Hepatopulmonary Syndrome and Muscle Wasting in rats with Biliary Cirrhosis
Abstract
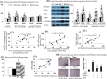
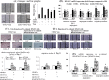
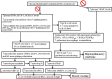
Thalidomide can modulate the TNFα-NFκB and iNOS pathway, which involve in the pathogenesis of hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) and muscle wasting in cirrhosis. In bile duct ligated-cirrhotic rats, the increased circulating CD16+ (inflammatory) monocytes and its intracellular TNFα, NFκB, monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP-1) and iNOS levels were associated with increased circulating MCP-1/soluable intercellular cell adehesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), pulmonary TNFα/NOx, up-regulated M1 polarization, exacerbated angiogenesis and hypoxemia (increased AaPO2) in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid and pulmonary homogenates. Meanwhile, a significant correlation was noted between circulating CD16+ monocyte/M1 (%) macrophages in BAL; M1 (%) macrophages in BAL/pulmonary iNOS mRNA expression; pulmonary iNOS mRNA expression/relative pulmonary MVD; pulmonary NOx level/AaPO2; circulating CD16+ monocyte/M1 (%) macrophages in muscle homogenates; 3-nitrotyrosine (representative of peroxynitrite) concentration/M1 (%) macrophages in muscle homogenates. The in vitro data demonstrated an iNOS-dependent inhibition of thalidomide on the TNFα-stimulated angiogenesis and myogenesis in human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (HPAECs) and C2C12 myoblasts. Significantly, the co-culture of CD16+ monocyte from different rats with HPAECs, or co-culture of supernatant of above mixed cultures with HPAECs or C2C12 myoblasts stimulated angiogenesis, migration and myogenesis. Our findings demonstrate that TNFα inhibitor thalidomide markedly diminishes the severity of experimental HPS and muscle wasting by down-regulation of common peripheral and local NFκB-iNOS pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Selective cyclooxygenase inhibition by SC-560 improves hepatopulmonary syndrome in cirrhotic rats.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 20;12(6):e0179809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179809. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28632747 Free PMC article.
-
Rosuvastatin improves hepatopulmonary syndrome through inhibition of inflammatory angiogenesis of lung.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Sep;129(6):449-60. doi: 10.1042/CS20140622. Epub 2015 May 5. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25940601
-
Intestinal endotoxemia plays a central role in development of hepatopulmonary syndrome in a cirrhotic rat model induced by multiple pathogenic factors.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Dec 21;13(47):6385-95. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i47.6385. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 18081228 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatopulmonary syndrome: update on recent advances in pathophysiology, investigation, and treatment.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Feb;28(2):213-9. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12061. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23190201 Review.
-
[A Cellular Pharmacological Approach to the Development of Drugs to Treat Muscle Wasting].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(10):1271-1275. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00091-3. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 30270271 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Protective Effects of Thalidomide on High-Glucose-Induced Podocyte Injury through In Vitro Modulation of Macrophage M1/M2 Differentiation.J Immunol Res. 2020 Aug 27;2020:8263598. doi: 10.1155/2020/8263598. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32908940 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory effects of thalidomide in an experimental brain death liver donor model.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 28;11(1):19221. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98538-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34584130 Free PMC article.
-
Key role of macrophages in the progression of hepatic fibrosis.Hepatol Commun. 2024 Dec 11;9(1):e0602. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000602. eCollection 2025 Jan 1. Hepatol Commun. 2024. PMID: 39670853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scattering polarimetry enables correlative nerve fiber imaging and multimodal analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 May 27;15(1):18493. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02762-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40425688 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of soluble PD-L1 in pleural effusions of mesothelioma patients: potential implications in the immune response and prognosis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Feb;147(2):459-468. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03457-7. Epub 2020 Nov 20. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33216211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nunes H. et al.. Role of nitric oxide in hepatopulmonary syndrome in cirrhotic Rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164, 879–885 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Schenk P. et al.. Prognostic significance of the hepatopulmonary syndrome in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 125, 1042–1052 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Swanson K. L., Wiesner R. H. & Krowka M. J. Natural history of hepatopulmonary syndrome: impact of liver transplantation. Hepatology 41, 1122–1129 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

