Test-retest reliability and concurrent validity of in vivo myelin content indices: Myelin water fraction and calibrated T1 w/T2 w image ratio
- PMID: 28009069
- PMCID: PMC5342928
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.23481
Test-retest reliability and concurrent validity of in vivo myelin content indices: Myelin water fraction and calibrated T1 w/T2 w image ratio
Abstract
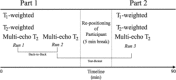
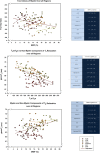
In an age-heterogeneous sample of healthy adults, we examined test-retest reliability (with and without participant repositioning) of two popular MRI methods of estimating myelin content: modeling the short spin-spin (T2 ) relaxation component of multi-echo imaging data and computing the ratio of T1 -weighted and T2 -weighted images (T1 w/T2 w). Taking the myelin water fraction (MWF) index of myelin content derived from the multi-component T2 relaxation data as a standard, we evaluate the concurrent and differential validity of T1 w/T2 w ratio images. The results revealed high reliability of MWF and T1 w/T2 w ratio. However, we found significant correlations of low to moderate magnitude between MWF and the T1 w/T2 w ratio in only two of six examined regions of the cerebral white matter. Notably, significant correlations of the same or greater magnitude were observed for T1 w/T2 w ratio and the intermediate T2 relaxation time constant, which is believed to reflect differences in the mobility of water between the intracellular and extracellular compartments. We conclude that although both methods are highly reliable and thus well-suited for longitudinal studies, T1 w/T2 w ratio has low criterion validity and may be not an optimal index of subcortical myelin content. Hum Brain Mapp 38:1780-1790, 2017. © 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: MRI; Simpson paradox; T2 relaxation; brain water mobility; white matter.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Aboitiz F, Scheibel AB, Fisher RS, Zaidel E (1992): Fiber composition of the human corpus callosum. Brain Res 598:143–153. - PubMed
-
- Alonso‐Ortiz E, Levesque IR, Pike GB (2015): MRI‐based myelin water imaging: A technical review. Magn Reson Med 73:70–81. - PubMed
-
- Ansari KA, Loch J (1975): Decreased myelin basic protein content of the aged human brain. Neurology 25:1045–1050. - PubMed
-
- Baltes PB, Nesselroade, JR (1979): History and rational of longitudinal research In: Nesselroade JR, Baltes PB, editors. Longitudinal research in the study of behavior and development. New York: Academic Press; pp 1–39.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

