Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PRL2 Mediates Notch and Kit Signals in Early T Cell Progenitors
- PMID: 28009085
- PMCID: PMC5367971
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.2559
Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PRL2 Mediates Notch and Kit Signals in Early T Cell Progenitors
Abstract
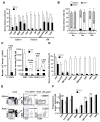
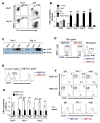
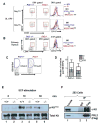
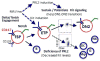
The molecular pathways regulating lymphoid priming, fate, and development of multipotent bone marrow hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) that continuously feed thymic progenitors remain largely unknown. While Notch signal is indispensable for T cell specification and differentiation, the downstream effectors are not well understood. PRL2, a protein tyrosine phosphatase that regulates hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and self-renewal, is highly expressed in murine thymocyte progenitors. Here we demonstrate that protein tyrosine phosphatase PRL2 and receptor tyrosine kinase c-Kit are critical downstream targets and effectors of the canonical Notch/RBPJ pathway in early T cell progenitors. While PRL2 deficiency resulted in moderate defects of thymopoiesis in the steady state, de novo generation of T cells from Prl2 null hematopoietic stem cells was significantly reduced following transplantation. Prl2 null HSPCs also showed impaired T cell differentiation in vitro. We found that Notch/RBPJ signaling upregulated PRL2 as well as c-Kit expression in T cell progenitors. Further, PRL2 sustains Notch-mediated c-Kit expression and enhances stem cell factor/c-Kit signaling in T cell progenitors, promoting effective DN1-DN2 transition. Thus, we have identified a critical role for PRL2 phosphatase in mediating Notch and c-Kit signals in early T cell progenitors. Stem Cells 2017;35:1053-1064.
Keywords: Early T lineage progenitors; Notch; PRL2; T cell progenitors; Thymopoiesis; c-Kit.
© 2016 AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that no conflict interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PRL2/PTP4A2 phosphatase is important for hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal.Stem Cells. 2014 Jul;32(7):1956-67. doi: 10.1002/stem.1672. Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 24753135 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role for c-kit (CD117) in T cell lineage commitment and early thymocyte development in vitro.Eur J Immunol. 2006 Mar;36(3):526-32. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535760. Eur J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16482516
-
Notch1 and IL-7 receptor interplay maintains proliferation of human thymic progenitors while suppressing non-T cell fates.J Immunol. 2006 Sep 15;177(6):3711-20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.6.3711. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16951331
-
Differential requirements for Wnt and Notch signaling in hematopoietic versus thymic niches.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Aug;1266:78-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06626.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22901260 Review.
-
Eliciting the T cell fate with Notch.Semin Immunol. 2010 Oct;22(5):254-60. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2010.04.011. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Semin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20627765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual-Specificity Phosphatase 15 (DUSP15) Modulates Notch Signaling by Enhancing the Stability of Notch Protein.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 May;58(5):2204-2214. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02254-0. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33417224
-
BMP-4 and BMP-7 Inhibit EMT in a Model of Anterior Subcapsular Cataract in Part by Regulating the Notch Signaling Pathway.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Apr 3;64(4):12. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.4.12. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 37043340 Free PMC article.
-
PRL3-DDX21 Transcriptional Control of Endolysosomal Genes Restricts Melanocyte Stem Cell Differentiation.Dev Cell. 2020 Aug 10;54(3):317-332.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.06.013. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Dev Cell. 2020. PMID: 32652076 Free PMC article.
-
PRL-2 phosphatase is required for vascular morphogenesis and angiogenic signaling.Commun Biol. 2020 Oct 23;3(1):603. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01343-z. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 33097786 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatase PRL2 promotes AML1-ETO-induced acute myeloid leukemia.Leukemia. 2017 Jun;31(6):1453-1457. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.67. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Leukemia. 2017. PMID: 28220038 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Godfrey DI, Kennedy J, Suda T, Zlotnik A. A developmental pathway involving four phenotypically and functionally distinct subsets of CD3-CD4-CD8- triple-negative adult mouse thymocytes defined by CD44 and CD25 expression. J Immunol. 1993;150:4244–4252. - PubMed
-
- Waskow C, Paul S, Haller C, Gassmann M, Rodewald HR. Viable c-Kit(W/W) mutants reveal pivotal role for c-kit in the maintenance of lymphopoiesis. Immunity. 2002;17:277–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

