Low Prevalence of Vitamin D Insufficiency among Nepalese Infants Despite High Prevalence of Vitamin D Insufficiency among Their Mothers
- PMID: 28009810
- PMCID: PMC5188478
- DOI: 10.3390/nu8120825
Low Prevalence of Vitamin D Insufficiency among Nepalese Infants Despite High Prevalence of Vitamin D Insufficiency among Their Mothers
Abstract
Background: Describing vitamin D status and its predictors in various populations is important in order to target public health measures.
Objectives: To describe the status and predictors of vitamin D status in healthy Nepalese mothers and infants.
Methods: 500 randomly selected Nepalese mother and infant pairs were included in a cross-sectional study. Plasma 25(OH)D concentrations were measured by LC-MS/MS and multiple linear regression analyses were used to identify predictors of vitamin D status.
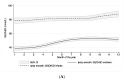
Results: Among the infants, the prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency (25(OH)D <50 nmol/L) and deficiency (<30 nmol/L) were 3.6% and 0.6%, respectively, in contrast to 59.8% and 14.0% among their mothers. Infant 25(OH)D concentrations were negatively associated with infant age and positively associated with maternal vitamin D status and body mass index (BMI), explaining 22% of the variability in 25(OH)D concentration. Global solar radiation, maternal age and BMI predicted maternal 25(OH)D concentration, explaining 9.7% of its variability.
Conclusion: Age and maternal vitamin D status are the main predictors of vitamin D status in infants in Bhaktapur, Nepal, who have adequate vitamin D status despite poor vitamin D status in their mothers.
Keywords: 25(OH)D; Nepal; infants; lactating mothers; season; vitamin D status.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dawodu A., Agarwal M., Hossain M., Kochiyil J., Zayed R. Hypovitaminosis D and vitamin D deficiency in exclusively breast-feeding infants and their mothers in summer: A justification for vitamin D supplementation of breast-feeding infants. J. Pediatr. 2003;142:169–173. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2003.63. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhalala U., Desai M., Parekh P., Mokal R., Chheda B. Subclinical hypovitaminosis D among exclusively breastfed young infants. Indian Pediatr. 2007;44:897–901. - PubMed
-
- Sachan A., Gupta R., Das V., Agarwal A., Awasthi P.K., Bhatia V. High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among pregnant women and their newborns in northern India. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005;81:1060–1064. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

