Parental Style and Its Association With Substance Use in Argentinean Youth
- PMID: 28010167
- PMCID: PMC5577981
- DOI: 10.1080/10826084.2016.1245337
Parental Style and Its Association With Substance Use in Argentinean Youth
Abstract
Background: In Europe and the United States, family relationships and parenting behavior can influence youth substance use, but less is known about their influence in Latin American countries.
Objective: To explore whether parenting behavior is associated with substance use among Latin American youth.
Methods: A cross-sectional, school-based survey of middle-school youth (n = 3172) in three Argentinian cities queried tobacco, alcohol, and drug use using items adapted from global youth surveys. Parenting behavior was assessed with previously validated items that tapped into demandingness and responsiveness, separately for mothers and fathers. Multilevel logistic regression models assessed associations between parenting behavior and substance use after adjusting for student characteristics, socioeconomic indicators, sensation seeking, and smoking amongst peers and family members.
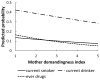
Results: Substance use prevalence was 10% for current smoking, 32% for current drinking alcohol, 17% for past 30-day binge drinking (≥5 drinks), and 8% for previous year illicit drug use (marijuana or cocaine). Greater maternal demandingness was independently associated with lower likelihood of current smoking (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] = 0.77; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.64-0.92), current drinking (AOR = 0.81; 95% CI: 0.71-0.92), binge drinking (AOR = 0.77; 95% CI: 0.66-0.99, and drug use (AOR = 0.71; 95% CI: 0.61-0.83). No other parenting behavior were independently associated with substance use, except for paternal demandingness and binge drinking (AOR = 0.84; 95% CI: 0.74-0.97). For all outcomes, no interactions were found between parenting behavior and student gender.
Conclusions: Among Argentine adolescents, maternal demandingness was the strongest and most consistent correlate of substance use, regardless of adolescent substance use behavior or gender.
Keywords: Adolescents; Argentina; Latin America; parenting; substance use.
Figures
References
-
- Alderete E, Kaplan CP, Gregorich SE, Mejia R, Perez-Stable EJ. Smoking behavior and ethnicity in Jujuy, Argentina: evidence from a low-income youth sample. Substance Use & Misuse. 2009;44(5):632–646. http://doi.org/10.1080/10826080902809717. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ackard DM, Neumark-Sztainer D, Story M, Perry C. Parent–child connectedness and behavioral and emotional health among adolescents. American journal of preventive medicine. 2006;30(1):59–66. - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Rosenthal S, Leonhardt D, Kollar L, Succop P, Burklow K, Biro F. Relationship between perceived parental monitoring and young adolescent girls’ sexual and substance use behaviors. Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology. 1999;12(1):17–22. - PubMed
-
- Baumrind D. The influence of parenting style on adolescent competence and substance use. The Journal of Early Adolescence. 1991;11(1):56–95.
-
- Becoña E, Calafat A, Fernández-Hermida JR, Juan M, Sumnall H, Mendes F, Gabrhelík R. Parental permissiveness, control, and affect and drug use among adolescents. Psicothema. 2013;25(3):292–298. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
