Emergence of miR-34a in radiation therapy
- PMID: 28010900
- PMCID: PMC5199215
- DOI: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2016.11.017
Emergence of miR-34a in radiation therapy
Abstract
Expressions of many microRNAs (miRNAs) in response to ionizing radiation (IR) have already been investigated and some of them seem to play an important role in the tumor radioresistance, normal tissue radiotoxicity or as predictive biomarkers to radiation. miR-34a is an emerging miRNA in recent radiobiology studies. Here, we review this miR-34 family member by detailing its different roles in radiation response and we will discuss about the role that it can play in radiation treatment. Thus, we will show that IR regulates miR-34a by increasing its expression. We will also highlight different biological processes involved in cellular response to IR and regulated by miR-34a in order to demonstrate the role it can play in tumor radio-response or normal tissue radiotoxicity as a radiosensitizer or radioprotector. miR-34a is poised to assert itself as an important player in radiobiology and should become more and more important in radiation therapy management.
Keywords: Biodosimetry; Biomarkers; Ionizing radiation; Oncology; Radiotherapy; Radiotoxicity; miR-34a.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
statement None
Figures
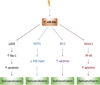
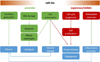
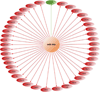
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

