The enduring patency of primary inferior vena cava repair
- PMID: 28011005
- PMCID: PMC5404996
- DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.11.006
The enduring patency of primary inferior vena cava repair
Abstract
Background: Inferior vena cava repair after planned and unplanned venotomy is performed by either interposition bypass, patch venopasty, or lateral venorrhaphy and primary repair. Primary repair of the inferior vena cava avoids the use of foreign material and allows an all-autologous repair in an expeditious fashion. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the utility of inferior vena cava repair, determine the degree of inferior vena cava stenosis, and examine clinical outcomes after primary repair.
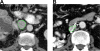
Methods: We conducted a single-center retrospective review of patients who underwent primary inferior vena cava repairs between January 2002 and January 2014 at a tertiary care center. Primary repair followed lateral venorrhaphy for tumor extraction or for repair of an iatrogenic inferior vena cava injury. Patient demographics, cross-sectional vena cava dimensions, and patient outcomes were tabulated.
Results: In total, 47 (30 men and 17 women) patients underwent primary inferior vena cava repair (median age 58 years, range 31-83 years). Twenty-six patients (15 men and 11 women) underwent en bloc radical nephrectomy, inferior vena cava tumor thrombus extraction, and primary lateral venorrhaphy (median age 61 years, range 39-83 years). The majority, 92% of these patients, had renal cell carcinoma on final pathology, with a median follow-up period of 39 months (range 1-108 months). Twenty-one patients (15 men and 6 women) underwent primary repair for iatrogenic inferior vena cava injury (median age 54 years, range 31-82 years). The median follow-up period was 18.5 months (3-110 months). Clinic follow-up with postoperative imaging was obtained in 76.9% of those undergoing tumor thrombus extraction (n = 20) and 76.2% of those undergoing repair of an iatrogenic injury (n = 16). Overall, there was a 13% infrarenal inferior vena cava diameter loss, 17% inferior vena cava diameter loss at the level of the renal veins, and 10% suprarenal inferior vena cava diameter loss when comparing postoperative with preoperative imaging. All patients remained asymptomatic; therefore, inferior vena cava narrowing associated with primary repair was clinically insignificant.
Conclusion: Primary inferior vena cava repair is associated with less than 20% inferior vena cava diameter loss and does not compromise venous outflow from the extremities. Primary inferior vena cava repair is a safe and expeditious technique that provides excellent clinical outcomes and long-term patency.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
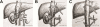
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Reese AC, Whitson JM, Meng MV. Natural history of untreated renal cell carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus. Urol Oncol. 2013;31:1305–9. - PubMed
-
- Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Canfield S, Dabestani S, Hofmann F, Hora M, et al. EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: 2014 update. Eur Urol. 2015;67:913–24. - PubMed
-
- Tomita TM, Rodriguez HE, Hoel AW, Ho KJ, Pearce WH, Eskandari MK. Intraoperative vascular surgery assistance is a crucial hospital asset. JAMA Surg. 2016 in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

