Temporal bone paragangliomas: 15 years experience
- PMID: 28011121
- PMCID: PMC9442861
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2016.11.001
Temporal bone paragangliomas: 15 years experience
Abstract
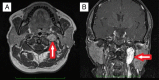
Introduction: Temporal bone paragangliomas (TBPs) are benign tumors arising from neural crest cells located along the jugular bulbus and the tympanic plexus. In general surgical excision, radiotherapy and wait-and-scan protocols are the main management modalities for TBPs.
Objective: In this paper we aim to present our clinical experience with TBPs and to review literature data.
Methods: The patients who were operated for tympanomastoid paraganglioma (TMP) or tympanojugular paraganglioma (TJP) in our clinic in the last 15 years were enrolled in the study. A detailed patient's charts review was performed retrospectively.
Results: There were 18 (52.9%) cases with TMPs and 16 (47.1%) cases with TJPs, a total of 34 patients operated for TBPs in this time period. The mean age was 50.3± 11.7 (range 25-71 years). The most common presenting symptoms were tinnitus and hearing loss for both TMPs and TJPs. Gross total tumor resection was achieved in 17 (94.4%) and 10 (62.5%) cases for TMPs and TJPs, respectively. Five patients (31.2%) with TJP experienced facial palsy following the operation. For all the patients the mean follow-up period was 25.8 months (range 4-108 months).
Conclusion: In conclusion, based on our findings and literature review, total surgical excision alone or with preoperative embolization is the main treatment modality for TBPs. However radiotherapy, observation protocol and subtotal resection must be considered in cases of preoperative functioning cranial nerves, large tumors and advanced age.
Introdução: Paragangliomas do osso temporal (POT) são tumores benignos derivados de células da crista neural localizadas ao longo do bulbo jugular e do plexo timpânico. Em geral, a excisão cirúrgica, a radioterapia e os protocolos de acompanhamento com estudos por imagem são as principais modalidades de conduta para o POT.
Objetivo: Apresentar nossa experiência clínica com POT e revisar os dados da literatura.
Método: Os pacientes que foram submetidos a cirurgia para paraganglioma timpanomastoideo (PTM) ou paraganglioma timpanojugular (PTJ) em nossa clínica nos últimos 15 anos foram incluídos no estudo. Realizou-se retrospectivamente uma revisão detalhada dos prontuários dos pacientes.
Resultados: Houve 18 (52,9%) casos com PTM e 16 (47,1%) casos com PTJ, portanto, um total de 34 pacientes operados para POT nesse período. A idade média foi de 50,3 ± 11,7 (intervalo de 25-71 anos). O sinais e sintomas de apresentação mais comuns foram o zumbido e perda auditiva, tanto para PTM quanto para PTJ. A ressecção tumoral completa foi obtida em 17 (94,4%) e 10 (62,5%) casos para PTM e PTJ, respectivamente. Cinco pacientes (31,2%) com PTJ apresentaram paralisia facial decorrente da cirurgia. Para todos os pacientes o tempo médio de seguimento foi de 25,8 meses (intervalo 4-108 meses).
Conclusão: Com base nos nossos dados e na revisão da literatura, a excisão cirúrgica total isolada ou com embolização pré-operatória é a principal modalidade de tratamento para POT. No entanto, a radioterapia, o protocolo de observação e a ressecção subtotal devem ser considerados no caso de nervos cranianos funcionais no pré-operatório, grandes tumores e idade avançada.
Keywords: Paraganglioma do osso temporal; Paraganglioma timpanojugular; Paraganglioma timpanomastóideo; Temporal bone paraganglioma; Tympanojugular paraganglioma; Tympanomastoid paraganglioma.
Copyright © 2016 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long-Term Outcome and Comparison of Treatment Modalities of Temporal Bone Paragangliomas.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 11;13(20):5083. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205083. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680232 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on Temporal Bone Paragangliomas.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2023 Oct;24(10):1392-1407. doi: 10.1007/s11864-023-01127-7. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37556048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microsurgical treatment of large and giant tympanojugular paragangliomas.Surg Neurol Int. 2014 Dec 11;5:179. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.146833. eCollection 2014. Surg Neurol Int. 2014. PMID: 25593763 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical management of tympanojugular paragangliomas using the flexible CO2 laser.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Dec;279(12):5623-5630. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07416-5. Epub 2022 May 5. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35511294 Free PMC article.
-
Paragangliomas of the head and neck: diagnosis and treatment.Fam Cancer. 2005;4(1):55-9. doi: 10.1007/s10689-004-2154-z. Fam Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15883711 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Outcome and Comparison of Treatment Modalities of Temporal Bone Paragangliomas.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 11;13(20):5083. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205083. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680232 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on Temporal Bone Paragangliomas.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2023 Oct;24(10):1392-1407. doi: 10.1007/s11864-023-01127-7. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37556048 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Myssiorek D., Ferlito A., Silver C.E., Rodrigo J.P., Baysal B.E., Fagan J.J., et al. Screening for familial paragangliomas. Oral Oncol. 2008;44:532–537. - PubMed
-
- Erickson D., Kudva Y.C., Ebersold M.J., Thompson G.B., Grant C.S., van Heerden J.A., et al. Benign paragangliomas: clinical presentation and treatment outcomes in 236 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:5210–5216. - PubMed
-
- Pellitteri P.K., Rinaldo A., Myssiorek D., Gary Jackson C., Bradley P.J., Devaney K.O., et al. Paragangliomas of the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 2004;40:563–575. - PubMed
-
- Düzlü M., Ileri F., Yılmaz M., Poyraz A. Co-existence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and sinonasal paraganglioma: a case report. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2011;21:298–302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

