A developmental transcriptomic analysis of Pax1 and Pax9 in embryonic intervertebral disc development
- PMID: 28011632
- PMCID: PMC5312110
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.023218
A developmental transcriptomic analysis of Pax1 and Pax9 in embryonic intervertebral disc development
Abstract
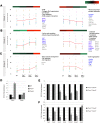
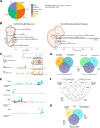
Pax1 and Pax9 play redundant, synergistic functions in the patterning and differentiation of the sclerotomal cells that give rise to the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs (IVD) of the axial skeleton. They are conserved in mice and humans, whereby mutation/deficiency of human PAX1/PAX9 has been associated with kyphoscoliosis. By combining cell-type-specific transcriptome and ChIP-sequencing data, we identified the roles of Pax1/Pax9 in cell proliferation, cartilage development and collagen fibrillogenesis, which are vital in early IVD morphogenesis. Pax1 is up-regulated in the absence of Pax9, while Pax9 is unaffected by the loss of Pax1/Pax9 We identified the targets compensated by a single- or double-copy of Pax9 They positively regulate many of the cartilage genes known to be regulated by Sox5/Sox6/Sox9 and are connected to Sox5/Sox6 by a negative feedback loop. Pax1/Pax9 are intertwined with BMP and TGF-B pathways and we propose they initiate expression of chondrogenic genes during early IVD differentiation and subsequently become restricted to the outer annulus by the negative feedback mechanism. Our findings highlight how early IVD development is regulated spatio-temporally and have implications for understanding kyphoscoliosis.
Keywords: BMP; Intervertebral disc; Pax1; Pax9; Sox trio; TGF-B.
© 2017. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Akiyama H., Chaboissier M.-C., Martin J. F., Schedl A. and de Crombrugghe B. (2002). The transcription factor Sox9 has essential roles in successive steps of the chondrocyte differentiation pathway and is required for expression of Sox5 and Sox6. Genes Dev. 16, 2813-2828. 10.1101/gad.1017802 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baffi M. O., Slattery E., Sohn P., Moses H. L., Chytil A. and Serra R. (2004). Conditional deletion of the TGF-beta type II receptor in Col2a expressing cells results in defects in the axial skeleton without alterations in chondrocyte differentiation or embryonic development of long bones. Dev. Biol. 276, 124-142. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.08.027 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

