The Italian subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator survey: S-ICD, why not?
- PMID: 28011803
- PMCID: PMC5834027
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euw337
The Italian subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator survey: S-ICD, why not?
Abstract
Aims: A recommendation for a subcutaneous-implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (S-ICD) has been added to recent European Society of Cardiology Guidelines. However, the S-ICD is not ideally suitable for patients who need pacing. The aim of this survey was to analyse the current practice of ICD implantation and to evaluate the actual suitability of S-ICD.
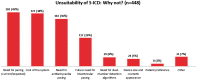
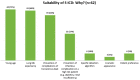
Methods and results: The survey 'S-ICD Why Not?' was an independent initiative taken by the Italian Heart Rhythm Society (AIAC). Clinical characteristics, selection criteria, and factors guiding the choice of ICD type were collected in consecutive patients who underwent ICD implantation in 33 Italian centres from September to December 2015. A cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device was implanted in 39% (369 of 947) of patients undergoing de novo ICD implantation. An S-ICD was implanted in 12% of patients with no CRT indication (62 of 510 with available data). S-ICD patients were younger than patients who received transvenous ICD, more often had channelopathies, and more frequently received their device for secondary prevention of sudden death. More frequently, the clinical reason for preferring a transvenous ICD over an S-ICD was the need for pacing (45%) or for antitachycardia pacing (36%). Nonetheless, only 7% of patients fulfilled conditions for recommending permanent pacing, and 4% of patients had a history of monomorphic ventricular tachycardia that might have been treatable with antitachycardia pacing.
Conclusion: The vast majority of patients needing ICD therapy are suitable candidates for S-ICD implantation. Nevertheless, it currently seems to be preferentially adopted for secondary prevention of sudden death in young patients with channelopathies.
Keywords: Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator; Indication; Pacing; Subcutaneous; Sudden death; Survey; Ventricular arrhythmias.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
References
-
- Priori SG, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Mazzanti A, Blom N, Borggrefe M, Camm J. et al. Task Force for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: The Task Force for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Europace 2015;17:1601–87. - PubMed
-
- Lee DS, Krahn AD, Healey JS, Birnie D, Crystal E, Dorian P. et al. ; Investigators of the Ontario ICD Database. Evaluation of early complications related to De Novo cardioverter defibrillator implantation insights from the Ontario ICD database. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55:774–82. - PubMed
-
- Ranasinghe I, Parzynski CS, Freeman JV, Dreyer RP, Ross JS, Akar JG. et al . Long-Term Risk for Device-Related Complications and Reoperations After Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Implantation: An Observational Cohort Study. Ann Intern Med 2016. May 3. doi: 10.7326/M15-2732. - PubMed
-
- Weiss R, Knight BP, Gold MR, Leon AR, Herre JM, Hood M. et al . Safety and efficacy of a totally subcutaneous implantable-cardioverter defibrillator. Circulation 2013;128:944–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials