Lentiviral Modulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Affects In Vivo LTP
- PMID: 28012021
- PMCID: PMC11482074
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-016-0455-z
Lentiviral Modulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Affects In Vivo LTP
Abstract
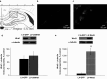
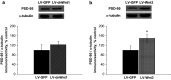
Wnt signaling is involved in hippocampal development and synaptogenesis. Numerous recent studies have been focused on the role of Wnt ligands in the regulation of synaptic plasticity. Inhibitors and activators of canonical Wnt signaling were demonstrated to decrease or increase, respectively, in vitro long-term potentiation (LTP) maintenance in hippocampal slices (Chen et al. in J Biol Chem 281:11910-11916, 2006; Vargas et al. in J Neurosci 34:2191-2202, 2014, Vargas et al. in Exp Neurol 264:14-25, 2015). Using lentiviral approach to down- and up-regulate the canonical Wnt signaling, we explored whether Wnt/β-catenin signaling is critical for the in vivo LTP. Chronic suppression of Wnt signaling induced an impairment of in vivo LTP expression 14 days after lentiviral suspension injection, while overexpression of Wnt3 was associated with a transient enhancement of in vivo LTP magnitude. Both effects were related to the early phase LTP and did not affect LTP maintenance. A loss-of-function study demonstrated decreased initial paired pulse facilitation ratio, β-catenin, and phGSK-3β levels. A gain-of-function study revealed not only an increase in PSD-95, β-catenin, and Cyclin D1 protein levels, but also a reduced phGSK-3β level and enhanced GSK-3β kinase activity. These results suggest a presynaptic dysfunction predominantly underlying LTP impairment while postsynaptic modifications are primarily involved in transient LTP amplification. This study is the first demonstration of the involvement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in synaptic plasticity regulation in an in vivo LTP model.
Keywords: GSK-3β; Hippocampus; LTP; Lentivirus; PSD-95; Paired pulse facilitation; Synaptic plasticity; Wnt signaling.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The GSK-3β/β-Catenin Signaling-Mediated Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Pathway Is Involved in Aluminum-Induced Impairment of Hippocampal LTP In Vivo.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021 Dec;199(12):4635-4645. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02582-9. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. PMID: 33462795
-
Hypoxic postconditioning activates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and protects against transient global cerebral ischemia through Dkk1 Inhibition and GSK-3β inactivation.FASEB J. 2019 Aug;33(8):9291-9307. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802633R. Epub 2019 May 23. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31120770
-
[Dexmedetomidine-mediated Wnt Pathway Inhibits Sevoflurane-induced Cognitive Impairment in Neonatal Rats].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2021 Apr 28;43(2):235-246. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.12913. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 33966704 Chinese.
-
Interactions among paired-pulse facilitation and post-tetanic and long-term potentiation in the mossy fiber-CA3 pathway in rat hippocampus.Synapse. 1996 Aug;23(4):302-11. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(199608)23:4<302::AID-SYN8>3.0.CO;2-B. Synapse. 1996. PMID: 8855515
-
LTD, LTP, and the sliding threshold for long-term synaptic plasticity.Hippocampus. 1996;6(1):35-42. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1996)6:1<35::AID-HIPO7>3.0.CO;2-6. Hippocampus. 1996. PMID: 8878740 Review.
Cited by
-
Alzheimer's Disease: An Overview of Major Hypotheses and Therapeutic Options in Nanotechnology.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Dec 29;11(1):59. doi: 10.3390/nano11010059. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33383712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Selective GSK3β Inhibitor, Tideglusib, Decreases Intermittent Access and Binge Ethanol Self-Administration in C57BL/6J Mice.Addict Biol. 2025 May;30(5):e70044. doi: 10.1111/adb.70044. Addict Biol. 2025. PMID: 40390305 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt3a/GSK3β/β-catenin Signalling Modulates Doxorubicin-associated Memory Deficits in Breast Cancer.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Aug;61(8):5441-5458. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03910-x. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38198045
-
Intact memory for local and distal cues in male and female rats that lack adult neurogenesis.PLoS One. 2018 May 22;13(5):e0197869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197869. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29787617 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt Signaling Mediates LTP-Dependent Spine Plasticity and AMPAR Localization through Frizzled-7 Receptors.Cell Rep. 2018 Apr 24;23(4):1060-1071. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.119. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29694885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderton BH, Dayanandan R, Killick R, Lovestone S (2000) Does dysregulation of the Notch and wingless/Wnt pathways underlie the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease? Mol Med Today 6:54–59 - PubMed
-
- Aoki K, Taketo MM (2008) Tissue-specific transgenic, conditional knockout and knock-in mice of genes in the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Methods Mol Biol 468:307–331 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

