Ammonia toxicity: from head to toe?
- PMID: 28012068
- PMCID: PMC8839071
- DOI: 10.1007/s11011-016-9938-3
Ammonia toxicity: from head to toe?
Abstract
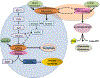
Ammonia is diffused and transported across all plasma membranes. This entails that hyperammonemia leads to an increase in ammonia in all organs and tissues. It is known that the toxic ramifications of ammonia primarily touch the brain and cause neurological impairment. However, the deleterious effects of ammonia are not specific to the brain, as the direct effect of increased ammonia (change in pH, membrane potential, metabolism) can occur in any type of cell. Therefore, in the setting of chronic liver disease where multi-organ dysfunction is common, the role of ammonia, only as neurotoxin, is challenged. This review provides insights and evidence that increased ammonia can disturb many organ and cell types and hence lead to dysfunction.
Keywords: Ammonia; Brain; Hepatic encephalopathy; Liver; Muscle; Toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
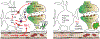
Similar articles
-
Multifactorial Effects on Different Types of Brain Cells Contribute to Ammonia Toxicity.Neurochem Res. 2017 Mar;42(3):721-736. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-1966-1. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 27286679 Review.
-
Identifying the direct effects of ammonia on the brain.Metab Brain Dis. 2009 Mar;24(1):95-102. doi: 10.1007/s11011-008-9112-7. Epub 2008 Dec 23. Metab Brain Dis. 2009. PMID: 19104924 Review.
-
Ammonia-induced stress response in liver disease progression and hepatic encephalopathy.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Nov;21(11):774-791. doi: 10.1038/s41575-024-00970-9. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39251708 Review.
-
L-Ornithine phenylacetate (OP): a novel treatment for hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy.Med Hypotheses. 2007;69(5):1064-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2006.12.061. Epub 2007 Apr 27. Med Hypotheses. 2007. PMID: 17467190
-
Rapid metabolic and bioenergetic adaptations of astrocytes under hyperammonemia - a novel perspective on hepatic encephalopathy.Biol Chem. 2021 Jul 30;402(9):1103-1113. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2021-0172. Print 2021 Aug 26. Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34331848 Review.
Cited by
-
Rare Pathogenic Variants in Pooled Whole-Exome Sequencing Data Suggest Hyperammonemia as a Possible Cause of Dementia Not Classified as Alzheimer's Disease or Frontotemporal Dementia.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jun 7;15(6):753. doi: 10.3390/genes15060753. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927689 Free PMC article.
-
Hypokalaemia - an active contributor to hepatic encephalopathy?Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Jun;38(5):1765-1768. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-01096-0. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 36326977
-
Calculation of Mass Transfer and Cell-Specific Consumption Rates to Improve Cell Viability in Bioink Tissue Constructs.Materials (Basel). 2021 Aug 5;14(16):4387. doi: 10.3390/ma14164387. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34442913 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic Encephalopathy: From Metabolic to Neurodegenerative.Neurochem Res. 2021 Oct;46(10):2612-2625. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03372-4. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 34129161 Review.
-
Ammonia transporter RhBG initiates downstream signaling and functional responses by activating NFκB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 30;121(31):e2314760121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2314760121. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39052834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdo AA (2006) An evidence-based update on hepatic encephalopathy. Saudi J Gastroenterol 12:8–15 - PubMed
-
- Agusti A, Cauli O, Rodrigo R, Llansola M, Hernández-Rabaza V, Felipo V (2011) p38 MAP kinase is a therapeutic target for hepatic encephalopathy in rats with portacaval shunts. Gut 60:1572–1579 - PubMed
-
- Alger BE, Nicoll RA (1983) Ammonia does not selectively block IPSPs in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J. Neurophysiol 49:1381–1391 - PubMed
-
- Ali R, Mittal G, Sultana S, Bhatnagar A (2012) Ameliorative potential of alpha-ketoglutaric acid (AKG) on acute lung injuries induced by ammonia inhalation in rats. Experimental Lung Research 38:435–444 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

