MHC class II alleles associated with Th1 rather than Th17 type immunity drive the onset of early arthritis in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 28012172
- PMCID: PMC7163699
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201646760
MHC class II alleles associated with Th1 rather than Th17 type immunity drive the onset of early arthritis in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
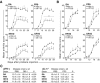
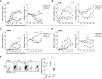
Polymorphisms in the MHC class II (MHCII) genes are strongly associated with rheumatoid arthritis, supporting the importance of autoreactive T helper (Th) cells for the development of this disease. Here, we used pristane-induced arthritis (PIA), induced by the non-antigenic hydrocarbon pristane, to study the impact of different MHCII alleles on T-cell activation and differentiation. In MHCII-congenic rats with disease-promoting MHCII alleles, pristane primarily induced activation of Th1 cells, whereas activated T cells were Th17 biased in rats with protective MHCII alleles. Neutralization of IFN-γ during T-cell activation abrogated the development of disease, suggesting that Th1 immunity is important for disease induction. Neutralization of IL-17, by contrast, suppressed arthritis only when performed in rats with established disease. Adoptive T-cell transfers showed that T cells acquired arthritogenic capacity earlier in strains with a prevailing Th1 response. Moreover, upon pristane injection, these strains exhibited more Ag-primed OX40+ and proliferating T cells of polyclonal origin. These data show that T cells are polarized upon the first encounter with peptide-MHCII complexes in an allele-dependent fashion. In PIA, the polyclonal expansion of autoreactive Th1 cells was necessary for the onset of arthritis, while IL-17 mediated immunity contributed to the progression to chronic disease.
Keywords: Animal models; Autoimmunity; Immune responses; MHC; Rheumatoid arthritis; T helper (Th) cells.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Mahdi, H. , Fisher, B. A. , Källberg, H. , Plant, D. , Malmström, V. , Rönnelid, J. , Charles, P. et al., Specific interaction between genotype, smoking and autoimmunity to citrullinated alpha‐enolase in the etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2009. 41: 1319–1324. doi: 10.1038/ng.480. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

