Galanin contributes to monoaminergic dysfunction and to dependent neurobehavioral comorbidities of epilepsy
- PMID: 28013000
- PMCID: PMC5285493
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.12.008
Galanin contributes to monoaminergic dysfunction and to dependent neurobehavioral comorbidities of epilepsy
Abstract
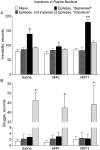
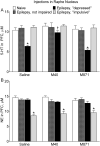
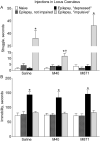
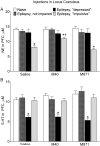
Status epilepticus (SE) in rats, along with chronic epilepsy, leads to the development of behavioral impairments resembling depressive disorder and/or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), thus reflecting respective comorbidities in epilepsy patients. Suppressed neurotransmitter tone in the raphe nucleus (RN)-prefrontal cortex (PFC) serotonergic pathway and in the locus coeruleus (LC)-PFC noradrenergic pathway underlies depressive- and impulsive-like behavioral deficits respectively. We examined possible mechanisms leading to the monoamine dysfunction in brainstem efferents, namely modulatory effects of the neuropeptide galanin on serotonin (5-HT) and norepinephrine (NE) signaling. SE was induced in young adult male Wistar rats by LiCl and pilocarpine. Epileptic rats were categorized vis-à-vis behavioral deficits as not impaired, "depressed" and "impulsive". Depressive- and impulsive-like behaviors were examined in the forced swimming test (FST). The strength of serotonergic transmission in RN-PFC and of noradrenergic transmission in LC-PFC was analyzed using in vivo fast scan cyclic voltammetry. Galanin receptor type 1 (GalR1)/type 2 (GalR2) antagonist M40, and a preferential GalR2 antagonist M871 were administered over 3days locally into either RN or LC by means of ALZET osmotic minipumps connected to locally implanted infusion cannulas. Intra-RN injection of M40 improved serotonergic tone and depressive-like behavior in epileptic "depressed" rats. Intra-LC injection of M40 improved noradrenergic tone and impulsive-like behavior in epileptic "impulsive" rats. The effects of M40 were only observed in impaired subjects. The treatment did not modify neurotransmission and behavior in naïve and epileptic not impaired rats; in "depressed" rats the effects were limited to serotonergic transmission and immobility, while in "impulsive" rats - to noradrenergic transmission and struggling behavior. Intra-RN administration of M871 exacerbated depressive-like behavior, but had no effects on any other of the examined parameters in any category of animals. These findings suggest that endogenous galanin, acting through GalR1 may be involved in the pathophysiology of epilepsy-associated depression and ADHD via inhibiting RN-PFC serotonergic and LC-PFC noradrenergic transmissions respectively.
Keywords: Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder; Comorbidity; Depression; Epilepsy; Galanin; Locus coeruleus; Norepinephrine; Prefrontal cortex; Raphe nucleus; Serotonin.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


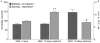
Similar articles
-
Effects of selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors on depressive- and impulsive-like behaviors and on monoamine transmission in experimental temporal lobe epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2016 Mar;57(3):506-15. doi: 10.1111/epi.13321. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Epilepsia. 2016. PMID: 26813337 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral impairments in rats with chronic epilepsy suggest comorbidity between epilepsy and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.Epilepsy Behav. 2014 Feb;31:267-75. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Epilepsy Behav. 2014. PMID: 24262783 Free PMC article.
-
Inherent vulnerabilities in monoaminergic pathways predict the emergence of depressive impairments in an animal model of chronic epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2017 Aug;58(8):e116-e121. doi: 10.1111/epi.13822. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Epilepsia. 2017. PMID: 28597913 Free PMC article.
-
[Domino principle--monoamines in bottom-view].Neuropsychopharmacol Hung. 2008 Jun;10(3):131-40. Neuropsychopharmacol Hung. 2008. PMID: 18956617 Review. Hungarian.
-
Galanin receptor antagonists : a potential novel pharmacological treatment for mood disorders.CNS Drugs. 2006;20(8):633-54. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200620080-00003. CNS Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16863269 Review.
Cited by
-
Home-cage monitoring ascertains signatures of ictal and interictal behavior in mouse models of generalized seizures.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 7;14(11):e0224856. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224856. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31697745 Free PMC article.
-
The ventrolateral medulla and medullary raphe in sudden unexpected death in epilepsy.Brain. 2018 Jun 1;141(6):1719-1733. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy078. Brain. 2018. PMID: 29608654 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Serum Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor, Nerve Growth Factor, Glial-derived Neurotrophic Factor and Galanin Levels in Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, and the Effect of 10 Weeks Methylphenidate Treatment.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2022 Nov 30;20(4):635-648. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2022.20.4.635. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36263639 Free PMC article.
-
The Challenge of Pharmacotherapy in Children and Adolescents with Epilepsy-ADHD Comorbidity.Clin Drug Investig. 2018 Jan;38(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s40261-017-0585-1. Clin Drug Investig. 2018. PMID: 29071470 Review.
-
The diverse role of the raphe 5-HTergic systems in epilepsy.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 Nov;43(11):2777-2788. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-00918-2. Epub 2022 May 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35614227 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chandley MJ, Ordway GA. Noradrenergic Dysfunction in Depression and Suicide. In: Dwivedi Y, editor. The Neurobiological Basis of Suicide. Boca Raton (FL): 2012. - PubMed
-
- Counts SE, McGuire SO, Sortwell CE, Crawley JN, Collier TJ, Mufson EJ. Galanin inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase expression in midbrain dopaminergic neurons. J Neurochem. 2002;83:442–451. - PubMed
-
- Cryan JF, Page ME, Lucki I. Differential behavioral effects of the antidepressants reboxetine, fluoxetine, and moclobemide in a modified forced swim test following chronic treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2005;182:335–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

