The blood transfer conductance for nitric oxide: Infinite vs. finite θNO
- PMID: 28013060
- PMCID: PMC5449205
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2016.12.007
The blood transfer conductance for nitric oxide: Infinite vs. finite θNO
Abstract
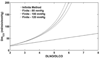
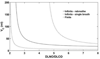
Whether the specific blood transfer conductance for nitric oxide (NO) with hemoglobin (θNO) is finite or infinite is controversial but important in the calculation of alveolar capillary membrane conductance (DmCO) and pulmonary capillary blood volume (VC) from values of lung diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) and nitric oxide (DLNO). In this review, we discuss the background associated with θNO, explore the resulting values of DmCO and VC when applying either assumption, and investigate the mathematical underpinnings of DmCO and VC calculations. In general, both assumptions yield reasonable rest and exercise DmCO and VC values. However, the finite θNO assumption demonstrates increasing VC, but not DmCO, with submaximal exercise. At relatively high, but physiologic, DLNO/DLCO ratios both assumptions can result in asymptotic behavior for VC values, and under the finite θNO assumption, DmCO values. In conclusion, we feel that the assumptions associated with a finite θNO require further in vivo validation against an established method before widespread research and clinical use.
Keywords: Alveolar capillary membrane conductance; Exercise; In vivo validation; Lung diffusing capacity; Pulmonary capillary blood volume.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypothesis: Why θNO could be finite in vitro but infinite in vivo.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2017 Jul;241:58-61. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2017.02.013. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28249804
-
Lung membrane conductance and capillary volume derived from the NO and CO transfer in high-altitude newcomers.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013 Jul 15;115(2):157-66. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01455.2012. Epub 2013 Apr 18. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013. PMID: 23599397
-
Pulmonary membrane diffusing capacity and capillary blood volume measured during exercise from nitric oxide uptake.Chest. 2001 Dec;120(6):1850-6. doi: 10.1378/chest.120.6.1850. Chest. 2001. PMID: 11742912
-
The blood transfer conductance for CO and NO.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2017 Jul;241:53-57. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2017.02.010. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28259748 Review.
-
Nitrogen monoxide and carbon monoxide transfer interpretation: state of the art.Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2017 Jul;37(4):357-365. doi: 10.1111/cpf.12316. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2017. PMID: 26576688 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous Measurement of Lung Diffusing Capacity and Pulmonary Hemodynamics Reveals Exertional Alveolar-Capillary Dysfunction in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Aug 17;10(16):e019950. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019950. Epub 2021 Aug 7. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34369164 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Alveolo-Capillary Gas Transfer Disturbances in Patients Recovering from COVID-19 Lung Disease.J Pers Med. 2024 Jul 10;14(7):738. doi: 10.3390/jpm14070738. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39063992 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of intrathoracic pressure, inhalation time, and breath hold time on lung diffusing capacity.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2018 Dec;258:69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2018.06.001. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29885374 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Inhaled Amiloride on Lung Fluid Clearance in Response to Normobaric Hypoxia in Healthy Individuals.High Alt Med Biol. 2017 Dec;18(4):343-354. doi: 10.1089/ham.2017.0032. Epub 2017 Sep 6. High Alt Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28876128 Free PMC article.
-
Double gas transfer factors (DLCO-DLNO) at rest in patients with congenital heart diseases correlates with their ventilatory response during maximal exercise.Int J Cardiol Congenit Heart Dis. 2022 Feb 19;8:100346. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcchd.2022.100346. eCollection 2022 Jun. Int J Cardiol Congenit Heart Dis. 2022. PMID: 39712052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borland C, Dunningham H, Bottrill F, Vuylsteke A. Can a membrane oxygenator be a model for lung NO and CO trannsfer? Journal of applied physiology. 2006;100:1527–1538. - PubMed
-
- Borland CD, Cox Y. Effect of varying alveolar oxygen partial pressure on diffusing capacity for nitric oxide and carbon monoxide, membrane diffusing capacity and lung capillary blood volume. Clinical science. 1991;81:759–765. - PubMed
-
- Borland CD, Higenbottam TW. A simultaneous single breath measurement of pulmonary diffusing capacity with nitric oxide and carbon monoxide. The European respiratory journal. 1989;2:56–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

