Baicalin Inhibits Renal Cell Apoptosis and Protects Against Acute Kidney Injury in Pediatric Sepsis
- PMID: 28013315
- PMCID: PMC5207012
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.899061
Baicalin Inhibits Renal Cell Apoptosis and Protects Against Acute Kidney Injury in Pediatric Sepsis
Abstract
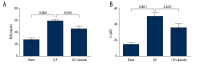
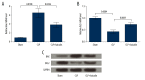
BACKGROUND Pediatric sepsis has high morbidity in children, may lead to acute kidney injury (AKI), and further aggravate the disease. Baicalin is a kind of flavonoid in Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi and has been reported to protect against several diseases, but its roles in septic AKI remain unclear. This study aimed to uncover the effects of baicalin in AKI during pediatric sepsis. MATERIAL AND METHODS Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (Cr) levels were detected in 50 pediatric patients, who underwent basic therapy with or without baicalin adjunctive therapy. Mouse sepsis models were constructed by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) and treated with baicalin intragastrically, after which BUN and Cr examination, TUNEL apoptosis assay, and expression analyses of BAX and BCL2 were performed. RESULTS Baicalin adjunctive therapy significantly decreased BUN and Cr levels in pediatric sepsis patients (P<0.05). CLP led to elevated BUN and Cr levels in the mouse model (P<0.01), indicating kidney injury accompanied by sepsis. Baicalin decreased BUN and Cr levels (P<0.05), and reduced the apoptotic cell percent in the renal tissue (P<0.05) of the CLP model. It inhibited BAX and promoted BCL2 in the renal tissue, which was consistent with cell apoptosis changes. CONCLUSIONS Baicalin is capable of suppressing renal cell apoptosis and protecting against AKI in pediatric sepsis. This study provides a potential adjunctive therapy for treating AKI in pediatric sepsis, and further research is necessary to reveal its deeper mechanisms.
Figures
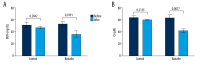

References
-
- Khilanani A, Mazwi M, Paquette ET. Pediatric sepsis in the global setting. Clinical Pediatric Emergency Medicine. 2014;15:193–203.
-
- Oliveira CF, Nogueira de Sá FR, Oliveira DSF, et al. Time- and fluid-sensitive resuscitation for hemodynamic support of children in septic shock: Barriers to the implementation of the American College of Critical Care Medicine/Pediatric Advanced Life Support Guidelines in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit in a Developing World. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2008;24:810–15. - PubMed
-
- Despond O, Proulx F, Carcillo JA, Lacroix J. Pediatric sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2001;13:247–53. - PubMed
-
- Kirkebøen KA, Strand OA. The role of nitric oxide in sepsis – an overview. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1999;43:275–88. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman JJ. A history of adjunctive glucocorticoid treatment for pediatric sepsis: Moving beyond steroid pulp fiction toward evidence-based medicine. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2007;8:530–39. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

