Differential effects of aprepitant, a clinically used neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist on the expression of conditioned psychostimulant versus opioid reward
- PMID: 28013351
- PMCID: PMC5266628
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-016-4504-6
Differential effects of aprepitant, a clinically used neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist on the expression of conditioned psychostimulant versus opioid reward
Abstract
Rationale: Neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) signaling modulates behaviors associated with psychostimulants and opioids. Psychostimulants, such as amphetamine (AMPH) and cocaine, bind to monoamine transporters and alter their functions. Both dopamine and norepinephrine transporters are regulated by NK1R activation suggesting a role for NK1R mediated catecholamine transporter regulation in psychostimulant-mediated behaviors.
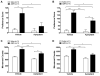
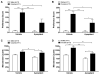
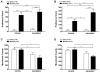
Objectives: The effect of in vivo administration of aprepitant (10 mg/kg) on the expression of AMPH (0.5 and 2 mg/kg) and cocaine (5 and 20 mg/kg)-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) as well as locomotor activation was examined in C57BL/6J mice. The effect of aprepitant on morphine (1 and 5 mg/kg)-induced CPP was also examined to identify the specific actions of aprepitant on psychostimulant versus opioid-induced behaviors.
Results: Aprepitant administration significantly attenuated the CPP expression and locomotor activation produced by AMPH and cocaine. In contrast, aprepitant significantly enhanced the expression of CPP produced by morphine while significantly suppressing the locomotor activity of the mice conditioned with morphine. Aprepitant by itself did not induce significant CPP or conditioned place aversion or locomotor activation or suppression.
Conclusions: Attenuation of AMPH or cocaine-induced CPP and locomotor activation by aprepitant suggests a role for NK1R signaling in psychostimulant-mediated behaviors. Stimulation of morphine-induced CPP expression and suppression of locomotor activity of morphine-conditioned mice suggest differential effects of NK1R antagonism on conditioned psychostimulant versus opioid reward. Collectively, these findings indicate that clinically used NK1R antagonist, aprepitant may serve as a potential therapeutic agent in the treatment of psychostimulant abuse.
Keywords: Amphetamine; Antagonist; Aprepitant; Cocaine; Conditioned place preference; Drug abuse; Morphine; Neurokinin-1 receptor; Opioids; Psychostimulants.
Figures
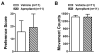
Similar articles
-
Neurokinin-1 Antagonism Distinguishes the Role of Norepinephrine Transporter from Dopamine Transporter in Mediating Amphetamine Behaviors.Pharmacology. 2021;106(11-12):597-605. doi: 10.1159/000518033. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Pharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34515205 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility to conditioned place preference induced by addictive drugs in mice of the C57BL/6 and DBA/2 inbred strains.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Sep;181(2):327-36. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-2259-6. Epub 2005 Oct 14. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15864555
-
Conditioned place preference and locomotor activity in response to methylphenidate, amphetamine and cocaine in mice lacking dopamine D4 receptors.J Psychopharmacol. 2010 Jun;24(6):897-904. doi: 10.1177/0269881109102613. Epub 2009 Mar 12. J Psychopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19282420 Free PMC article.
-
Psychostimulants, antidepressants and neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists ('motor disinhibitors') have overlapping, but distinct, effects on monoamine transmission: the involvement of L-type Ca2+ channels and implications for the treatment of ADHD.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Dec;87:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.03.021. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24727210 Review.
-
Ghrelin and ghrelin receptor modulation of psychostimulant action.Front Neurosci. 2013 Sep 25;7:171. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00171. Front Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24093007 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interference of norepinephrine transporter trafficking motif attenuates amphetamine-induced locomotor hyperactivity and conditioned place preference.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Jan;128:132-141. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.10.005. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28986281 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-nociceptive effects of dual neuropeptide antagonist therapy in mouse model of neuropathic and inflammatory pain.Korean J Pain. 2022 Apr 1;35(2):173-182. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.173. Korean J Pain. 2022. PMID: 35354680 Free PMC article.
-
Neurokinin-1 Antagonism Distinguishes the Role of Norepinephrine Transporter from Dopamine Transporter in Mediating Amphetamine Behaviors.Pharmacology. 2021;106(11-12):597-605. doi: 10.1159/000518033. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Pharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34515205 Free PMC article.
-
Aedes aegypti sialokinin facilitates mosquito blood feeding and modulates host immunity and vascular biology.Cell Rep. 2022 Apr 12;39(2):110648. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110648. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35417706 Free PMC article.
-
Threonine-53 Phosphorylation of Dopamine Transporter Dictates κ-Opioid Receptor-Mediated Locomotor Suppression, Aversion, and Cocaine Reward.J Neurosci. 2025 Jun 18;45(25):e0171252025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0171-25.2025. J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40393807
References
-
- Amadoro G, Pieri M, Ciotti MT, Carunchio I, Canu N, Calissano P, Zona C, Severini C. Substance P provides neuroprotection in cerebellar granule cells through Akt and MAPK/Erk activation: evidence for the involvement of the delayed rectifier potassium current. Neuropharmacology. 2007;52:1366–77. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

