Potentiation of the NO-cGMP pathway and blood flow responses during dynamic exercise in healthy humans
- PMID: 28013386
- PMCID: PMC5315588
- DOI: 10.1007/s00421-016-3523-7
Potentiation of the NO-cGMP pathway and blood flow responses during dynamic exercise in healthy humans
Abstract
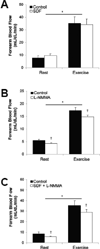
Purpose: Previous work has shown nitric oxide (NO) contributes to ~15% of the hyperemic response to dynamic exercise in healthy humans. This NO-mediated vasodilation occurs, in part, via increases in intracellular cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which is catabolized by phosphodiesterase. We sought to examine the effect of phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibition on forearm blood flow (FBF) responses to dynamic handgrip exercise in healthy humans and the role of NO. We hypothesized exercise hyperemia would be augmented by sildenafil citrate (SDF, PDE-5 inhibitor). We further hypothesized any effect of SDF on exercise hyperemia would be abolished with intra-arterial infusion of the NO synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NG-monomethyl arginine (L-NMMA).
Methods: FBF (Doppler ultrasound) was assessed at rest and during 5 min of dynamic forearm handgrip exercise at 15% of maximal voluntary contraction under control (saline) conditions and during 3 experimental protocols: (1) oral SDF (n = 10), (2) intra-arterial L-NMMA (n = 20), (3) SDF and L-NMMA (n = 10). FBF responses to intra-arterial sodium nitroprusside (NTP, NO donor) were also assessed.
Results: FBF increased with exercise (p < 0.01). Intra-arterial infusion of L-NMMA resulted in a reduction in exercise hyperemia (17 ± 1 to 15 ± 1 mL/dL/min, p < 0.01). Although the hyperemic response to NTP was augmented by SDF (area under the curve: 41 ± 7 vs 61 ± 11 AU, p < 0.01), there was no effect of SDF on exercise hyperemia (p = 0.33).
Conclusions: Despite improving NTP-mediated vasodilation, oral SDF failed to augment exercise hyperemia in young, healthy adults. These observations reflect a minor contribution of NO and the cGMP pathway during exercise hyperemia in healthy young humans.
Keywords: Blood flow; Cyclic GMP; Exercise; Nitric oxide; Regional; Sildenafil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition preserves exercise-onset vasodilator kinetics when NOS activity is reduced.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018 Feb 1;124(2):276-282. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00483.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 5. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018. PMID: 28982942 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of nitric oxide to exercise hyperemia in the human forearm.Vasc Med. 2002 Aug;7(3):163-8. doi: 10.1191/1358863x02vm439oa. Vasc Med. 2002. PMID: 12553738
-
Nitric oxide, but not vasodilating prostaglandins, contributes to the improvement of exercise hyperemia via ascorbic acid in healthy older adults.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Nov;299(5):H1633-41. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00614.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20817831 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term treatment with eicosapentaenoic acid improves exercise-induced vasodilation in patients with coronary artery disease.Hypertens Res. 2002 Nov;25(6):823-9. doi: 10.1291/hypres.25.823. Hypertens Res. 2002. PMID: 12484504
-
Physiological Impact and Clinical Relevance of Passive Exercise/Movement.Sports Med. 2019 Sep;49(9):1365-1381. doi: 10.1007/s40279-019-01146-1. Sports Med. 2019. PMID: 31264182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acute exercise inhibits gastric emptying of liquids in rats: influence of the NO-cGMP pathway.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018 Oct 4;51(11):e7541. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20187541. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018. PMID: 30304131 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary nitrate does not acutely enhance skeletal muscle blood flow and vasodilation in the lower limbs of older adults during single-limb exercise.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020 Jun;120(6):1357-1369. doi: 10.1007/s00421-020-04368-8. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32303829 Clinical Trial.
-
Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition preserves exercise-onset vasodilator kinetics when NOS activity is reduced.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018 Feb 1;124(2):276-282. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00483.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 5. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018. PMID: 28982942 Free PMC article.
-
Increased cGMP improves microvascular exercise training adaptations in diet-induced obesity.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2025 May 1;328(5):E711-E722. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00368.2024. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40204283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attina TM, Malatino LS, Maxwell SR, Padfield PL, Webb DJ. Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibition reverses impaired forearm exercise-induced vasodilatation in hypertensive patients. J Hypertens. 2008;26:501–507. - PubMed
-
- Bradley SJ, Kingwell BA, McConell GK. Nitric oxide synthase inhibition reduces leg glucose uptake but not blood flow during dynamic exercise in humans. Diabetes. 1999;48:1815–1821. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

