PK/PD Target Attainment With Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Using Monte Carlo Simulation in Patients With Various Degrees of Renal Function, Including Augmented Renal Clearance and End-Stage Renal Disease
- PMID: 28013453
- PMCID: PMC5336418
- DOI: 10.1007/s40121-016-0143-9
PK/PD Target Attainment With Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Using Monte Carlo Simulation in Patients With Various Degrees of Renal Function, Including Augmented Renal Clearance and End-Stage Renal Disease
Abstract
Introduction: Ceftolozane/tazobactam is an antibacterial agent with potent in vitro activity against Gram-negative pathogens, including many extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae and drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Because ceftolozane/tazobactam is primarily excreted renally, appropriate dose adjustments are needed for patients with renal impairment. Monte Carlo simulations were used to determine the probability of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic target attainment for patients with varying degrees of renal function, including augmented renal clearance (ARC) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) with hemodialysis.
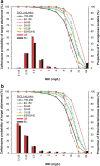
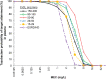
Methods: Monte Carlo simulations were conducted for 1000 patients with ARC and normal renal function, mild renal impairment, moderate renal impairment, or severe renal impairment, and for 5000 patients with ESRD. Simulated dosing regimens were based on approved doses for each renal function category. Attainment targets for ceftolozane were 24.8% (bacteriostasis), 32.2% (1-log kill; bactericidal), and 40% (2-log kill) fT > minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The target for tazobactam was to achieve a 20% fT > minimum effective concentration (MEC) at an MEC of 1 mg/L, which was derived from a neutropenic mouse thigh infection model and was confirmed by efficacy data from clinical studies for complicated intraabdominal infections and complicated urinary tract infections.
Results: In patients with ARC or normal renal function, ≥91% achieved bactericidal activity (32.2% fT > MIC) up to an MIC of 4 mg/L with a 1000-mg ceftolozane dose. In patients with renal impairment (mild, moderate, severe, ESRD), ≥93% achieved bactericidal activity up to an MIC of 8 mg/L. In patients of all renal function categories, the approved dosing regimens of tazobactam achieved ≥91% target attainment against a target of 20% fT > MEC.
Conclusions: At the approved dosing regimens for ceftolozane/tazobactam, ≥91% of patients in all renal function categories, including ARC (up to 200 mL/min) and ESRD, reached target attainment for bactericidal activity at MICs that correspond to susceptibility breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae and P. aeruginosa.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Ceftolozane/tazobactam; Complicated intraabdominal infection; Complicated urinary tract infection; ESRD; Gram-negative pathogens; Monte Carlo simulation; Renal impairment; Target attainment.
Figures

References
-
- Farrell DJ, Sader HS, Flamm RK, Jones RN. Ceftolozane/tazobactam activity tested against Gram-negative bacterial isolates from hospitalised patients with pneumonia in US and European medical centres (2012) Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014;43:533–539. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.01.032. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Farrell DJ, Flamm RK, Sader HS, Jones RN. Antimicrobial activity of ceftolozane-tazobactam tested against Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa with various resistance patterns isolated in U.S. hospitals (2011–2012) Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:6305–6310. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01802-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zerbaxa (ceftolozane and tazobactam) [prescribing information]. Whitehouse Station: Merck Sharp & Dohme, 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

