ATXN2 trinucleotide repeat length correlates with risk of ALS
- PMID: 28017481
- PMCID: PMC5302215
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.11.010
ATXN2 trinucleotide repeat length correlates with risk of ALS
Abstract
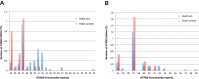
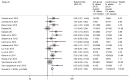
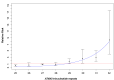
We investigated a CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the ATXN2 gene in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Two new case-control studies, a British dataset of 1474 ALS cases and 567 controls, and a Dutch dataset of 1328 ALS cases and 691 controls were analyzed. In addition, to increase power, we systematically searched PubMed for case-control studies published after 1 August 2010 that investigated the association between ATXN2 intermediate repeats and ALS. We conducted a meta-analysis of the new and existing studies for the relative risks of ATXN2 intermediate repeat alleles of between 24 and 34 CAG trinucleotide repeats and ALS. There was an overall increased risk of ALS for those carrying intermediate sized trinucleotide repeat alleles (odds ratio 3.06 [95% confidence interval 2.37-3.94]; p = 6 × 10-18), with an exponential relationship between repeat length and ALS risk for alleles of 29-32 repeats (R2 = 0.91, p = 0.0002). No relationship was seen for repeat length and age of onset or survival. In contrast to trinucleotide repeat diseases, intermediate ATXN2 trinucleotide repeat expansion in ALS does not predict age of onset but does predict disease risk.
Keywords: ALS; ATXN2; Age of onset; Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; CAG; Expansion; Exponential risk; Intermediate expansion; Risk; SCA2; Trinucleotide repeat; Triplet.
Copyright © 2016 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Abel O., Powell J.F., Andersen P.M., Al-Chalabi A. ALSoD: a user-friendly online bioinformatics tool for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis genetics. Hum. Mutat. 2012;33:1345–1351. - PubMed
-
- Al-Chalabi A., Calvo A., Chio A., Colville S., Ellis C.M., Hardiman O., Heverin M., Howard R.S., Huisman M.H., Keren N., Leigh P.N., Mazzini L., Mora G., Orrell R.W., Rooney J., Scott K.M., Scotton W.J., Seelen M., Shaw C.E., Sidle K.S., Swingler R., Tsuda M., Veldink J.H., Visser A.E., van den Berg L.H., Pearce N. Analysis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis as a multistep process: a population-based modelling study. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:1108–1113. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Chalabi A., Hardiman O. The epidemiology of ALS: a conspiracy of genes, environmental and time. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013;9:617–628. - PubMed
-
- Burnham K.P., Anderson D.R. Springer-Verlag; New York: 2002. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-theoretic Approach.
-
- Chen Y., Huang R., Yang Y., Chen K., Song W., Pan P., Li J., Shang H.F. Ataxin-2 intermediate-length polyglutamine: a possible risk factor for Chinese patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Aging. 2011;32:1925. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_G1000733/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L501529/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600974/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MALASPINA/APR13/817-791/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- G0900688/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- JONES/OCT15/958-799/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- G0300329/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0900635/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ALCHALABI-DOBSON/APR14/829-791/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- AL-CHALABI/APR15/844-791/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- MR/M008606/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L021803/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1100695/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- FRATTA/JAN15/946-795/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- G0501573/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0500289/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R35 NS097275/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MRF-060-0003-RG-SMITH/MRF_/MRF_/United Kingdom
- SHAW/NOV14/985-797/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

