A Histologic Basis for the Efficacy of SBRT to the lung
- PMID: 28017592
- PMCID: PMC7066985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.002
A Histologic Basis for the Efficacy of SBRT to the lung
Abstract
Purpose: Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is the standard of care for medically inoperable patients with early-stage NSCLC. However, NSCLC is composed of several histological subtypes and the impact of this heterogeneity on SBRT treatments has yet to be established.
Methods: We analyzed 740 patients with early-stage NSCLC treated definitively with SBRT from 2003 through 2015. We calculated cumulative incidence curves using the competing risk method and identified predictors of local failure using Fine and Gray regression.
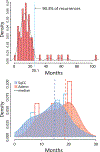
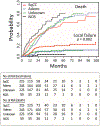
Results: Overall, 72 patients had a local failure, with a cumulative incidence of local failure at 3 years of 11.8%. On univariate analysis, squamous histological subtype, younger age, fewer medical comorbidities, higher body mass index, higher positron emission tomography standardized uptake value, central tumors, and lower radiation dose were associated with an increased risk for local failure. On multivariable analysis, squamous histological subtype (hazard ratio = 2.4 p = 0.008) was the strongest predictor of local failure. Patients with squamous cancers fail SBRT at a significantly higher rate than do those with adenocarcinomas or NSCLC not otherwise specified, with 3-year cumulative rates of local failure of 18.9% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 12.7-25.1), 8.7% (95% CI: 4.6-12.8), and 4.1% (95% CI: 0-9.6), respectively.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate an increased rate of local failure in patients with squamous cell carcinoma. Standard approaches for radiotherapy that demonstrate efficacy for a population may not achieve optimal results for individual patients. Establishing the differential dose effect of SBRT across histological groups is likely to improve efficacy and inform ongoing and future studies that aim to expand indications for SBRT.
Keywords: SABR; heterogeneity; personalized; precision.
Copyright © 2016 International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this study have no conflicts of interest pertaining to the conduct of this research.
Figures
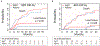
Comment in
-
The Relationship between Histology, Stage, and Type of Treatment in Patients with Early-Stage Lung Cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2017 May;12(5):e58-e59. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.01.024. J Thorac Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28434519 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
7-year follow-up after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer: Results of a phase 2 clinical trial.Cancer. 2017 Aug 15;123(16):3031-3039. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30693. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28346656 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A SUVmax-based propensity matched analysis of stereotactic body radiotherapy versus surgery in stage I non-small cell lung cancer: unveiling the role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in clinical decision-making.Clin Transl Oncol. 2018 Aug;20(8):1026-1034. doi: 10.1007/s12094-017-1819-7. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29327241
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy versus conventional radiation therapy in patients with early stage non-small cell lung cancer: an updated retrospective study on local failure and survival rates.Acta Oncol. 2013 Oct;52(7):1552-8. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2013.813635. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Acta Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23902274 Clinical Trial.
-
Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer: A critical literature review of predictive factors of relapse.Cancer Treat Rev. 2016 Nov;50:240-246. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016. PMID: 27768919 Review.
-
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Primer for Radiologists.Radiographics. 2018 Sep-Oct;38(5):1312-1336. doi: 10.1148/rg.2018170155. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Radiographics. 2018. PMID: 30074857 Review.
Cited by
-
Histology, Tumor Volume, and Radiation Dose Predict Outcomes in NSCLC Patients After Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy.J Thorac Oncol. 2018 Oct;13(10):1549-1559. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.06.007. Epub 2018 Jun 27. J Thorac Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29959060 Free PMC article.
-
Which patients benefit most from stereotactic body radiotherapy or surgery in medically operable non-small cell lung cancer? An in-depth look at patient characteristics on both sides of the debate.Thorac Cancer. 2019 Oct;10(10):1857-1867. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13160. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Thorac Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31389163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) improves local control and overall survival compared to conventionally fractionated radiation for stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Acta Oncol. 2018 Nov;57(11):1567-1573. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2018.1481292. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Acta Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29873277 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction uncertainty estimates elucidate the limitation of current NSCLC subtype classification in representing mutational heterogeneity.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 21;14(1):6779. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57057-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38514696 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Methylation as a Noninvasive Epigenetic Biomarker for the Detection of Cancer.Dis Markers. 2017;2017:3726595. doi: 10.1155/2017/3726595. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Dis Markers. 2017. PMID: 29038612 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ginsberg RJ, Rubinstein LV. Randomized trial of lobectomy versus limited resection for T1 N0 non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer Study Group. The Annals of thoracic surgery. September 1995;60(3):615–622; discussion 622–613. - PubMed
-
- Timmerman RD, Hu C, Michalski J, et al. Long-term Results of RTOG 0236: A Phase II Trial of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in the Treatment of Patients with Medically Inoperable Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. In: Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2014:S30.
-
- Videtic GM, Hu C, Singh AK, et al. A Randomized Phase 2 Study Comparing 2 Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Schedules for Medically Inoperable Patients With Stage I Peripheral Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: NRG Oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. November 15 2015;93(4):757–764. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crabtree TD, Denlinger CE, Meyers BF, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy versus surgical resection for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. August 2010;140(2):377–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

