Selective coupling of the S1P3 receptor subtype to S1P-mediated RhoA activation and cardioprotection
- PMID: 28017639
- PMCID: PMC5410967
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.12.008
Selective coupling of the S1P3 receptor subtype to S1P-mediated RhoA activation and cardioprotection
Abstract
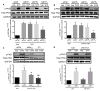
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), a bioactive lysophospholipid, is generated and released at sites of tissue injury in the heart and can act on S1P1, S1P2, and S1P3 receptor subtypes to affect cardiovascular responses. We established that S1P causes little phosphoinositide hydrolysis and does not induce hypertrophy indicating that it does not cause receptor coupling to Gq. We previously demonstrated that S1P confers cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion by activating RhoA and its downstream effector PKD. The S1P receptor subtypes and G proteins that regulate RhoA activation and downstream responses in the heart have not been determined. Using siRNA or pertussis toxin to inhibit different G proteins in NRVMs we established that S1P regulates RhoA activation through Gα13 but not Gα12, Gαq, or Gαi. Knockdown of the three major S1P receptors using siRNA demonstrated a requirement for S1P3 in RhoA activation and subsequent phosphorylation of PKD, and this was confirmed in studies using isolated hearts from S1P3 knockout (KO) mice. S1P treatment reduced infarct size induced by ischemia/reperfusion in Langendorff perfused wild-type (WT) hearts and this protection was abolished in the S1P3 KO mouse heart. CYM-51736, an S1P3-specific agonist, also decreased infarct size after ischemia/reperfusion to a degree similar to that achieved by S1P. The finding that S1P3 receptor- and Gα13-mediated RhoA activation is responsible for protection against ischemia/reperfusion suggests that selective targeting of S1P3 receptors could provide therapeutic benefits in ischemic heart disease.
Keywords: Cardioprotection; G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R); Phospholipase C (PLC); Protein kinase D (PKD); Ras homolog gene family member A (RhoA); Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P).
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



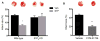
Similar articles
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate S1P2 and S1P3 receptor-mediated Akt activation protects against in vivo myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):H2944-51. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01331.2006. Epub 2007 Feb 9. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17293497
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 3 and RhoA signaling mediate inflammatory gene expression in astrocytes.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Jun 2;14(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0882-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 28577576 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-dependent inhibition of B16 melanoma cell migration and invasion via endogenous S1P2 G protein-coupled receptor. Requirement of inhibition of cellular RAC activity.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 29;278(35):32841-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305024200. Epub 2003 Jun 16. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12810709
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and biological activities in the cardiovascular system.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Sep;1781(9):483-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.04.003. Epub 2008 Apr 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18472021 Review.
-
Sphingosine kinase and sphingosine 1-phosphate in cardioprotection.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009 Mar;53(3):189-97. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181926706. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19247197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate levels are inversely associated with left ventricular and atrial chamber volume and cardiac mass in men : The Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP).Clin Res Cardiol. 2023 Nov;112(11):1587-1599. doi: 10.1007/s00392-023-02200-9. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Clin Res Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37097463 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Drug Targets for Ceramide Metabolism in Cardiovascular Disease.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022 Dec 2;9(12):434. doi: 10.3390/jcdd9120434. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022. PMID: 36547431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Density Lipoprotein Signaling via Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptors Safeguards Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats against Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Apr 3;16(4):497. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040497. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38675158 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing Roles of S1P3 Receptors in Myocardial Function.Cells. 2020 Jul 24;9(8):1770. doi: 10.3390/cells9081770. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32722120 Free PMC article.
-
Pepducin-mediated cardioprotection via β-arrestin-biased β2-adrenergic receptor-specific signaling.Theranostics. 2018 Sep 9;8(17):4664-4678. doi: 10.7150/thno.26619. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 30279730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carden DL, Granger DN. Pathophysiology of ischaemia-reperfusion injury. J Pathol. 2000;190:255–66. - PubMed
-
- Sattler KJ, Elbasan S, Keul P, Elter-Schulz M, Bode C, Graler MH, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate levels in plasma and HDL are altered in coronary artery disease. Basic Res Cardiol. 2010;105:821–32. - PubMed
-
- Theilmeier G, Schmidt C, Herrmann J, Keul P, Schafers M, Herrgott I, et al. High-density lipoproteins and their constituent, sphingosine-1-phosphate, directly protect the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo via the S1P3 lysophospholipid receptor. Circulation. 2006;114:1403–9. - PubMed
-
- Means CK, Xiao CY, Li Z, Zhang T, Omens JH, Ishii I, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate S1P2 and S1P3 receptor-mediated Akt activation protects against in vivo myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292:H2944–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

