Hippocalcin Promotes Neuronal Differentiation and Inhibits Astrocytic Differentiation in Neural Stem Cells
- PMID: 28017654
- PMCID: PMC5233403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.11.009
Hippocalcin Promotes Neuronal Differentiation and Inhibits Astrocytic Differentiation in Neural Stem Cells
Abstract
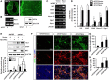
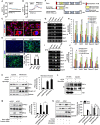
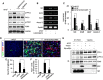
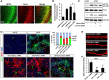
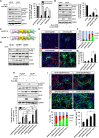
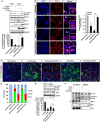
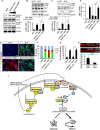
Hippocalcin (HPCA) is a calcium-binding protein that is restricted to nervous tissue and contributes to neuronal activity. Here we report that, in addition to inducing neurogenesis, HPCA inhibits astrocytic differentiation of neural stem cells. It promotes neurogenesis by regulating protein kinase Cα (PKCα) activation by translocating to the membrane and binding to phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1), which induces PKCα phosphorylation. We also found that phospholipase D1 (PLD1) is implicated in the HPCA-mediated neurogenesis pathway; this enzyme promotes dephosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3[Y705]), which is necessary for astrocytic differentiation. Moreover, we found that the SH2-domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase 1 (SHP-1) acts upstream of STAT3. Importantly, this SHP-1-dependent STAT3-inhibitory mechanism is closely involved in neurogenesis and suppression of gliogenesis by HPCA. Taken together, these observations suggest that HPCA promotes neuronal differentiation through activation of the PKCα/PLD1 cascade followed by activation of SHP-1, which dephosphorylates STAT3(Y705), leading to inhibition of astrocytic differentiation.
Keywords: SH2-domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1); gliogenesis; hippocalcin (HPCA); neural stem cells; neurogenesis; phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1); phospholipase D1 (PLD1); signal transducers and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3).
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Banno Y., Nemoto S., Murakami M., Kimura M., Ueno Y., Ohguchi K., Hara A., Okano Y., Kitade Y., Onozuka M. Depolarization-induced differentiation of PC12 cells is mediated by phospholipase D2 through the transcription factor CREB pathway. J. Neurochem. 2008;104:1372–1386. - PubMed
-
- Boncoeur E., Bouvet G.F., Migneault F., Tardif V., Ferraro P., Radzioch D., de Sanctis J.B., Eidelman D., Govindaraju K., Dagenais A. Induction of nitric oxide synthase expression by lipopolysaccharide is mediated by calcium-dependent PKCalpha-beta1 in alveolar epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2013;305:L175–L184. - PubMed
-
- Burgoyne R.D., O'Callaghan D.W., Hasdemir B., Haynes L.P., Tepikin A.V. Neuronal Ca2+-sensor proteins: multitalented regulators of neuronal function. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:203–209. - PubMed
-
- Cao F., Hata R., Zhu P., Nakashiro K., Sakanaka M. Conditional deletion of Stat3 promotes neurogenesis and inhibits astrogliogenesis in neural stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010;394:843–847. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

