A simple analytic method for estimating T2 in the knee from DESS
- PMID: 28017730
- PMCID: PMC5360502
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2016.12.018
A simple analytic method for estimating T2 in the knee from DESS
Abstract
Purpose: To introduce a simple analytical formula for estimating T2 from a single Double-Echo in Steady-State (DESS) scan.
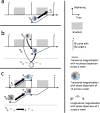
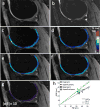
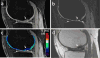
Methods: Extended Phase Graph (EPG) modeling was used to develop a straightforward linear approximation of the relationship between the two DESS signals, enabling accurate T2 estimation from one DESS scan. Simulations were performed to demonstrate cancellation of different echo pathways to validate this simple model. The resulting analytic formula was compared to previous methods for T2 estimation using DESS and fast spin-echo scans in agar phantoms and knee cartilage in three volunteers and three patients. The DESS approach allows 3D (256×256×44) T2-mapping with fat suppression in scan times of 3-4min.
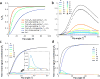
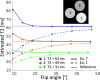
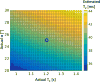
Results: The simulations demonstrated that the model approximates the true signal very well. If the T1 is within 20% of the assumed T1, the T2 estimation error was shown to be less than 5% for typical scans. The inherent residual error in the model was demonstrated to be small both due to signal decay and opposing signal contributions. The estimated T2 from the linear relationship agrees well with reference scans, both for the phantoms and in vivo. The method resulted in less underestimation of T2 than previous single-scan approaches, with processing times 60 times faster than using a numerical fit.
Conclusion: A simplified relationship between the two DESS signals allows for rapid 3D T2 quantification with DESS that is accurate, yet also simple. The simplicity of the method allows for immediate T2 estimation in cartilage during the MRI examination.
Keywords: Cartilage; DESS; Osteoarthritis; T(2).
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bruder H, Fischer H, Graumann R, Deimling M. A New Steady-State Imaging Sequence for Simultaneous Acquisition of Two MR Images with Clearly Different Contrasts. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1988;7:35–42. - PubMed
-
- Redpath TW, Jones RA. FADE - A New Fast Imaging Sequence. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1988;6:224–234. - PubMed
-
- Lee SY, Cho ZH. Fast SSFP Gradient Echo Sequence for Simultaneous Acquisitions of FID and Echo Signals. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1988;8:142–150. - PubMed
-
- Moran CJ, Saranathan M, Nnewihe AN, Granlund KL, Alley MT, Daniel BL, Hargreaves BA. High resolution images of the breast. European Journal of Radiology. 2012;81S1:S101–S103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

