Lymphadenectomy with Optimum of 29 Lymph Nodes Retrieved Associated with Improved Survival in Advanced Gastric Cancer: A 25,000-Patient International Database Study
- PMID: 28017807
- PMCID: PMC5606192
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.12.015
Lymphadenectomy with Optimum of 29 Lymph Nodes Retrieved Associated with Improved Survival in Advanced Gastric Cancer: A 25,000-Patient International Database Study
Abstract
Background: Gastric adenocarcinoma is an aggressive disease with frequent lymph node (LN) metastases for which lymphadenectomy results in a survival benefit. In the US, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend D2 lymphadenectomy or a minimum of 15 LNs retrieved. However, retrieval of only 15 LNs is considered by most international guidelines as inadequate. We sought to evaluate the survival benefits associated with a more complete lymphadenectomy.
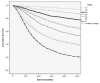
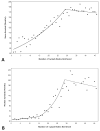
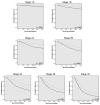
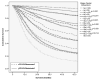
Study design: An international database was constructed by combining gastric cancer cases from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program database (n = 13,932) and the Yonsei University Gastric Cancer database (n = 11,358) (total n = 25,289). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was performed along with Joinpoint analysis to obtain the optimal number of LNs to retrieve based on survival. Prognostic significance of number of nodes retrieved was then confirmed with univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results: Analysis for both mean and median survival yielded 29 LNs removed as the Joinpoint. This was confirmed with multivariate analysis, where 15 retrieved LNs cutoff fell out of the model and 29 retrieved LNs remained intact, with a hazard ratio of 0.799 (95% CI 0.759 to 0.842; p < 0.001). Stage-stratified Kaplan-Meier analysis for a cutoff point of 29 LNs also demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in survival.
Conclusions: Joinpoint analysis has allowed for the creation of a model demonstrating the point at which additional dissection would not provide additional benefit. This large international dataset analysis demonstrates that the maximal survival advantage is seen by performing a lymphadenectomy with a minimum of 29 LNs retrieved.
Copyright © 2016 American College of Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Discussion.J Am Coll Surg. 2017 Apr;224(4):555-556. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2017.01.026. J Am Coll Surg. 2017. PMID: 28343498 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006 Jul 6;355(1):11–20. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J, et al. Chemoradiotherapy after surgery compared with surgery alone for adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. N Engl J Med. 2001 Sep 6;345(10):725–30. - PubMed
-
- Bang YJ, Kim YW, Yang HK, et al. Adjuvant capecitabine and oxaliplatin for gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy (CLASSIC): a phase 3 open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012 Jan 28;379(9813):315–21. - PubMed
-
- Sakuramoto S, Sasako M, Yamaguchi T, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer with S-1, an oral fluoropyrimidine. N Engl J Med. 2007 Nov 1;357(18):1810–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

