Recent advances in hyaluronic acid-decorated nanocarriers for targeted cancer therapy
- PMID: 28017836
- PMCID: PMC5413407
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2016.12.009
Recent advances in hyaluronic acid-decorated nanocarriers for targeted cancer therapy
Abstract
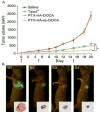
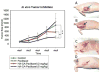
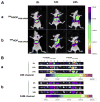
The cluster-determinant 44 (CD44) receptor has a high affinity for hyaluronic acid (HA) binding and is a desirable receptor for active targeting based on its overexpression in cancer cells compared with normal body cells. The nanocarrier affinity can be increased by conjugating drug-loaded carriers with HA, allowing enhanced cancer cell uptake via the HA-CD44 receptor-mediated endocytosis pathway. In this review, we discuss recent advances in HA-based nanocarriers and micelles for cancer therapy. In vitro and in vivo experiments have repeatedly indicated HA-based nanocarriers to be a target-specific drug and gene delivery platform with great promise for future applications in clinical cancer therapy.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, et al. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Mayol L, et al. Amphiphilic hyaluronic acid derivatives toward the design of micelles for the sustained delivery of hydrophobic drugs. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;102:110–116. - PubMed
-
- Matsumura Y, Maeda H. A New concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent Smancs. Cancer Res. 1986;46:6387–6392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

