Exercise, adipokines and pediatric obesity: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 28017965
- PMCID: PMC5382285
- DOI: 10.1038/ijo.2016.230
Exercise, adipokines and pediatric obesity: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background/objective: Adipokines are involved in the etiology of diabetes, insulin resistance, and the development of atherosclerosis and other latent-onset complications. The objective of this meta-analysis was to determine the effectiveness of exercise interventions on adipokines in pediatric obesity.
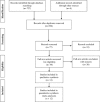
Subjects/methods: A computerized search was made using three databases. The analysis was restricted to studies that examined the effect of exercise interventions on adipokines (adiponectin, leptin, resistin and visfatin) in pediatric obesity (6-18 years old). Fourteen randomized controlled trials (347 youths) were included. Weighted mean difference (WMD) and 95% confidence intervals were calculated.
Results: Exercise was associated with a significant increase in adiponectin (WMD=0.882 μg ml-1, 95% CI, 0.271-1.493) but did not alter leptin and resistin level. Likewise, exercise intensity and change in body fat; as well as total exercise program duration, duration of the sessions, and change in body fat all significantly influenced the effect of exercise on adiponectin and leptin, respectively.
Conclusions: Exercise seems to increase adiponectin levels in childhood obesity. Our results also suggested that exercise on its own, without the concomitant presence of changes in body composition levels, does not affect leptin levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kershaw EE, Flier JS. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 2548–2556. - PubMed
-
- Ronti T, Lupattelli G, Mannarino E. The endocrine function of adipose tissue: an update. Clin Endocrinol 2006; 64: 355–365. - PubMed
-
- Barseghian A, Gawande D, Bajaj M. Adiponectin and vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011; 57: 761–770. - PubMed
-
- Sabbatini AR, Fontana V, Laurent S, Moreno H. An update on the role of adipokines in arterial stiffness and hypertension. J Hypertens 2015; 33: 435–444. - PubMed
-
- Gulcelik NE, Usman A, Gürlek A. Role of adipocytokines in predicting the development of diabetes and its late complications. Endocrine 2009; 36: 397–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

